Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
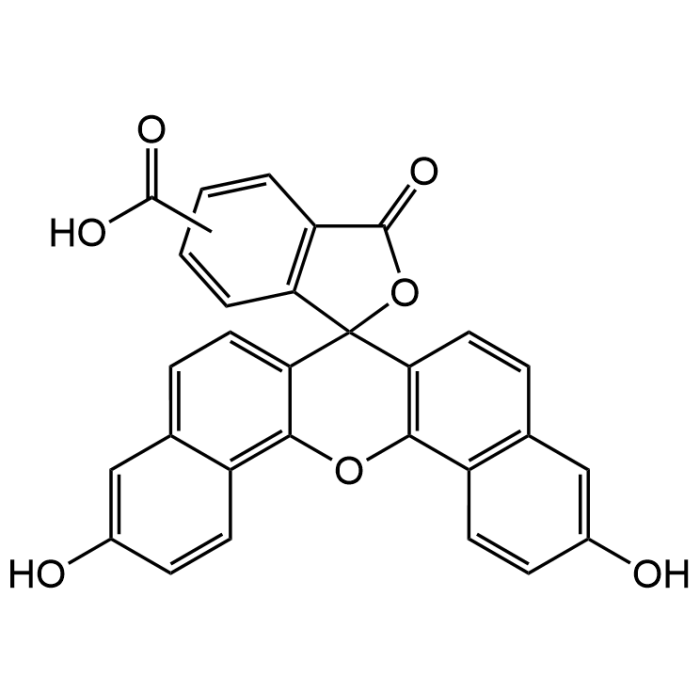
5(6)-Carboxynaphthofluorescein
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CNF |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C29H16O7 |
| MW | 476.43 |
| CAS | 128724-35-6 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥90% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Deep blue to deep violet powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or methanol (5mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ANUHNEJUELPITC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OC(=O)c1ccc2c(c1)C(=O)OC23c4ccc5cc(O)ccc5c4Oc6c3ccc7cc(O)ccc67.OC(=O)c8ccc9C(=O)OC%10(c%11ccc%12cc(O)ccc%12c%11Oc%13c%10ccc%14cc(O)ccc%13%14)c9c8 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
5(6)-Carboxynaphthofluorescein (CNF) is a fluorescent NIR emitting pH indicator with red fluorescence at pH 9 (Spectral: Ex/Em: 598/668 nm). The fluorescence shifs to shorter wavelengths (Ex/Em: 512/567nm) at neutral or acidic pH environments. Spectral data: λex=512nm; λem=567nm (acid/neutral); λex=598nm; λem=668nm (basic). CNF shows good sensitivity in an alkaline pH range and it can be exploited in the construction of fiber-optic pH sensors. CNF has been used as an intravesicular pH probe for the colorimetric detection of activity, selectivity and cooperativity of ion channels. CNF has been used to design a luminescent probe for determination of pH, based on a Forster resonance energy transfer (FRET) system, combining a europium chelate as the donor and CNF as a pH sensitive acceptor. The FRET system enables referenced pH detection in an exceptional broad dynamic range from pH 3 to 9.
(1) A. Song, et al.; Anal. Chem. 69, 863 (1997) | (2) S.M. Butterfield, et al.; Org. Biomol. Chem. 7, 1784 (2009) | (3) R.J. Meier, et al.; Chem. Commun. 51, 6145 (2015) | (4) E. Poehler, et al., Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 408, 2927 (2016) | (5) D.A. Jankowska, et al.; Biosens. Bioelectr. 87, 312 (2017) | (6) S. Nevolova, et al.; Biotech. J. 14, 1800144 (2019)





