Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
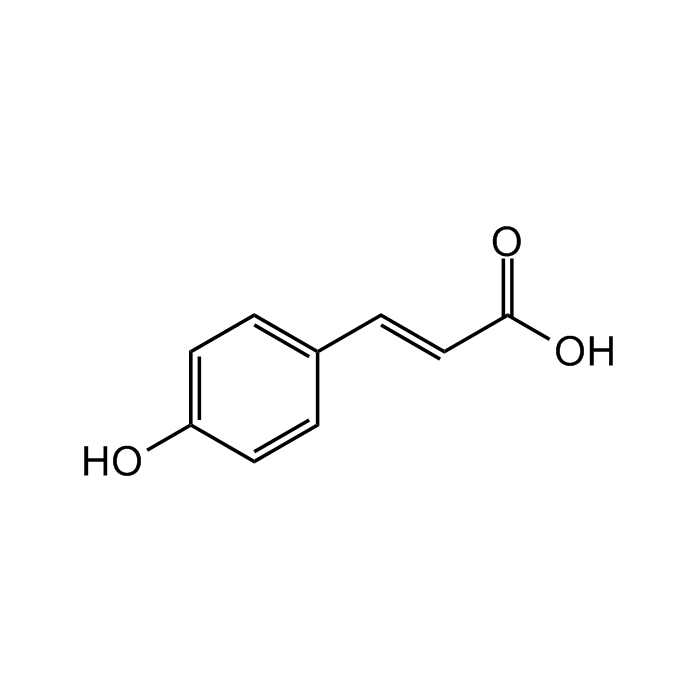
p-Coumaric acid
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | para-Coumaric Acid; trans-p-Coumaric Acid; trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid; (E)-3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C9H8O3 |
| MW | 164.16 |
| CAS | 501-98-4 |
| RTECS | GD9095000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (30 mg/ml), DMSO (15mg/ml) or DMF (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | NGSWKAQJJWESNS-ZZXKWVIFSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=CC=C(/C=C/C(O)=O)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
p-Coumaric acid is mainly a plant metabolite which exhibits antioxidant, antimicrobial, antitumor, antiangiogenic, antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic, neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties. It shows bactericidal/quorum sensing activity by damaging bacterial cell membrane and by interacting with bacterial DNA. It prevents metabolic syndromes through the activation of brown adipose tissue (BAT), linked to UCP1 upregulation, with accelerated burning of fatty acids and glucose, leading to enhanced the energy expenditure and thermogenesis. Also used in proteomics, e.g. in western blot, p-coumaric is used as an enhancer in chemiluminescent substrates. Used in cosmetics as a skin-lightening compound, due to its antimelanogenic effects, based on its potent competitive inhibition of tyrosinase.
(1) C. Luceri, et al.; Br. J. Nutr. 97, 458 (2007) | (2) C. Haan & I. Behrmann; J. Immunol. Meth. 318, 11 (2007) | (3) S.F. Bodini, et al.; Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 49, 551 (2009) | (4) D. Dolores & C.Y. Cheng; Spermatogenesis 1, 121 (2011) | (5) D. Stojkovic, et al.; J. Sci. Food Agric. 93, 3205 (2013) | (6) S.J. Pragasam & M. Rasool; Inflamm. Res. 62, 489 (2013) | (7) S.J. Pragasam, et al.; Inflammation 36, 169 (2013) | (8) C.S. Kong, et al.; Phytother. Res. 27, 317 (2013) | (9) S. Shailasree, et al.; Mol. Neurobiol. 51, 119 (2015) | (10) V. Amalan, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 84, 230 (2016) | (11) K. Pei, et al.; J. Sci. Food Agric. 96, 2952 (2016) (Review) | (12) A. Abdel-Moneim, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 105, 1091 (2018) | (13) S.H. Sharma, et al.; Chem. Biol. Interact. 291, 16 (2018) | (14) R. Sakamula, et al.; Metab. Brain Dis. 33, 765 (2018) | (15) Y.C. Boo; Antioxidants 8, 275 (2019) (Review) | (16) X. Hu, et al.; Front. Oncol. 10, 558414 (2020) | (17) X. Han, et al.; FASEB J. 34, 7810 (2020) | (18) M.F. Abazari, et al.; Mini Rev. Med. Chem. (epub ahead of print) (2021) (Review)





