Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
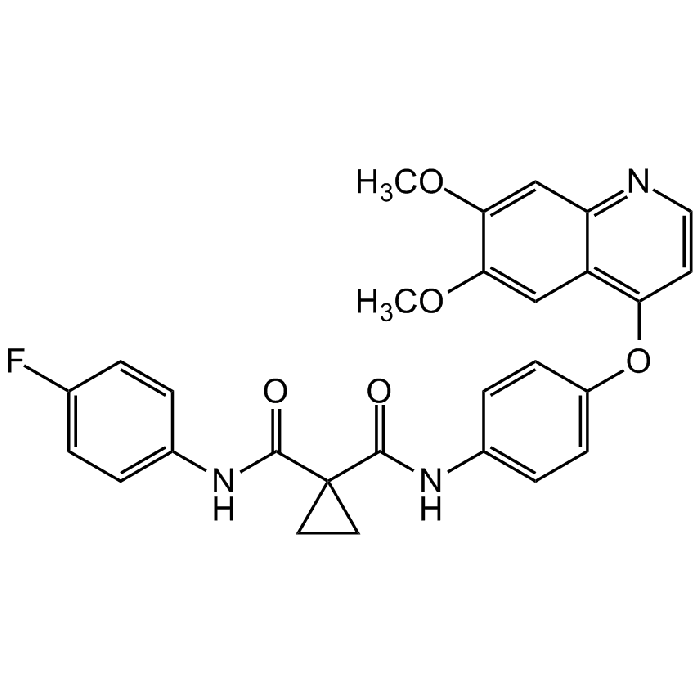
Cabozantinib
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BMS-907351; XL184 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C28H24FN3O5 |
| MW | 501.5 |
| CAS | 849217-68-1 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml). Slightly soluble in ethanol. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ONIQOQHATWINJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(NC1=CC=C(OC2=C3C=C(C(OC)=CC3=NC=C2)OC)C=C1)C4(C(NC5=CC=C(C=C5)F)=O)CC4 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Cabozantinib is a potent multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor of endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) (IC50=0.035nM), the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met (IC50=1.3nM), AXL (IC50=7nM), fms like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) (IC50=11.3nM), mast/stem cell growth factor (KIT) (IC50=4.6nM), RET (IC50=5.2nM), tyrosine-protein kinase receptor (TIE-2) (IC50=14.3nM) and RON (IC50=124nM). Cabozantinib reduces cell proliferation and vascular density. It also induces apoptosis and intratumoral hypoxia. Cabozantinib exhibits dose-related tumor growth inhibition, tumor regression, angiogenesis and/or metastasis inhibition in a broad range of preclinical tumor models. The anticancer compound cabozantinib has undergone clinical trial in a broad number of cancers, including thyroid carcinoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, melanoma, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular cancer, renal cell carcinoma and glioblastoma.
(1) Y. Zhang, et al.; IDrugs 13, 112 (2010) | (2) R. Kurzrock, et al.; J. Clin. Oncol. 29, 2660 (2011) | (3) F.M. Yakes, et al.; Mol. Canc. Ther. 10, 2298 (2011) | (4) S. Roy, et al.; Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 15, 37 (2015) (Review) | (5) N.M. Tannir, et al.; Curr. Oncol. Rep. 19, 14 (2017) (Review) | (6) C. Grullich; Recent Res. Cancer Res. 211, 67 (2018) (Review) | (7) J.N. Markowitz & K.M. Fancher;; Pharmacotherapy 38, 357 (2018) (Review) | (8) A. Desai & E.J. Small; Future Oncol. 15, 2337 (2019) (Review) | (9) J. Trojan; Drugs 80, 1203 (2020) (Review)





