Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
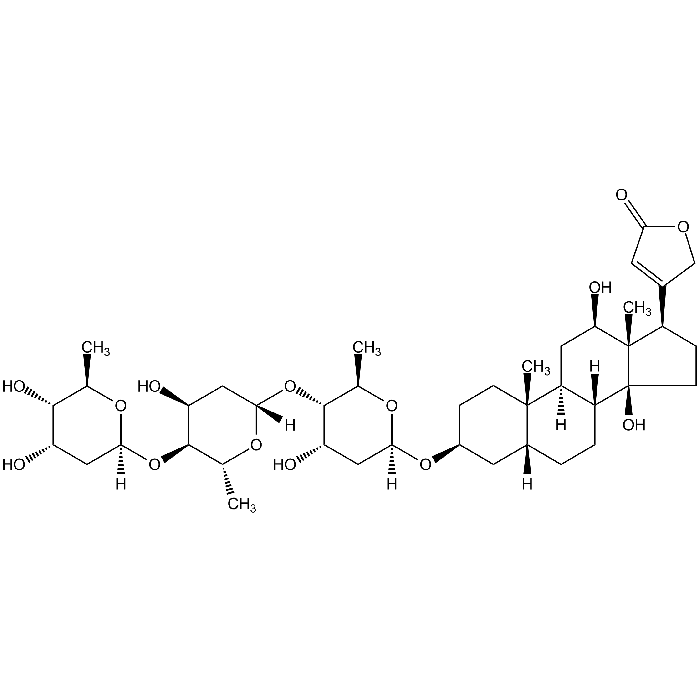
Digoxin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 12β-Hydroxydigitoxin; NSC 95100 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C41H64O14 |
| MW | 780.94 |
| CAS | 20830-75-5 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (100mM) or methanol. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | LTMHDMANZUZIPE-PUGKRICDSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(C[C@H](O)[C@H](O[C@@]2([H])C[C@H](O)[C@H](O[C@@]3([H])C[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)O3)[C@@H](C)O2)[C@@H](C)O1)O[C@H]1CC[C@@]2(C)[C@]([H])(CC[C@]3([H])[C@]2([H])C[C@@H](O)[C@]2(C)[C@H](CC[C@]32O)C2=CC(=O)OC2)C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Cardiac glycoside from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. It is used to treat cardiac arrhythmias. It is often used as a model substrate of P-glycoprotein (Pgp) (0.01-10µM) and an inhibitor of Na+/K+-ATPase. Inhibits membrane-bound α-subunits of the Na+/K+ ATPase pump in myocytes. The primary mechanism of action involves inhibition of the Na+/K+ ATPase, mainly in the myocardium. This inhibition causes an increase in intracellular sodium levels, resulting in a reversal of the action of the sodium-calcium exchanger, which causes an increase in the intracellular calcium concentration. This leads to a decrease in heart rate and increased storage of calcium in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, causing a corresponding increase in the release of calcium during each action potential.
(1) R.G. Woolfson, et al.; Kidney Int. 46, 297 (1994) | (2) S. Reddy, et al.; Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 12, 233 (1997) | (3) K. Kjeldsen & H. Bundgaard; Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 986, 702 (2003) | (4) M. Gheorghiade, et al.; Circulation 109, 2959 (2004) | (5) M. Ehle, et al.; Crit. Pathw. Cardiol. 10, 93 (2011) | (6) R.J. Biggar; Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 2133 (2012) | (7) A.M. Nader & D.R. Foster; J. Clin. Pharmacol. 54, 3 (2014) | (8) G.A. Ewy; Am. J. Med. 128, 1272 (2015)