Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
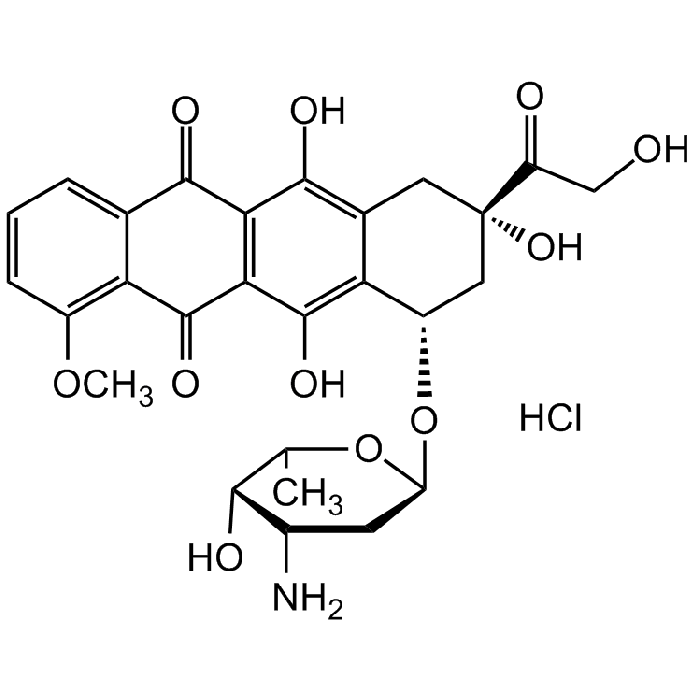
Doxorubicin hydrochloride
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DOX; Hydroxydaunorubicin; Adriamycin; NSC 123127 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C27H29NO11 . HCl |
| MW | 579.98 |
| CAS | 25316-40-9 |
| RTECS | QI9295900 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98 (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Orange to light red powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or water (20mg/ml). Slightly soluble in methanol. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | MWWSFMDVAYGXBV-RUELKSSGSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1C2=C(C(O)=C([C@@H](O[C@H]3C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O3)C[C@@](C(CO)=O)(O)C4)C4=C2O)C(C5=C(OC)C=CC=C51)=O.Cl |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Doxorubicin, a broad spectrum anthracycline antibiotic, inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis in mammalian cells and has been shown to be a very effective anti-tumor agent. Doxorubicin binds to nucleic acids by intercalating the DNA double helix and stabilizing topoisomerase II cleavage complexes, leading to DNA strand breaks at specific doxorubicin-induced sites and formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells. It also been shown to evict histones leading to chromatin damage. Doxorubicin induces apoptosis by inducing the accumulation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein and has been shown to have immunosuppressive properties. DOX can reduce mitochondrial NADH accumulation and impair oxidative phosphorylation in heart tissues, events associated with reduced glucose uptake. Doxorubicin can also induce the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pore, resulting in the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, thus explaining DOX-mediated apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Doxorubicin is a substrate of MRP1. Doxorubicin shows antimalarial activity and has been shown to inhibit parasite growth. Doxorubicin is used in the treatment of non-Hodgkin′s lymphoma and other cancers. Doxorubicin is naturally fluorescent with λex at 480nm and λem at 600nm. The fluorescent property has been exploited for the measurement of drug efflux pump activities as well as resolving the important question of intracellular localization of various multidrug resistance proteins and the role of subcellular organelles (Golgi and lysosome) in the sequestration of drugs and its implication in drug resistant phenotypes.
(1) H.G. Keizer, et al.; Pharmacol. Ther. 47, 219 (1990) (Review) | (2) S. Patel, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 658 (1997) | (3) E. Lorenzo, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 10883 (2002) | (4) S. Wang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25535 (2004) | (5) C. Carvalho, et al.; Curr. Med. Chem. 16, 3267 (2009) (Review) | (6) C.F. Thorn, et al.; Pharmacogenet. Genom. 21, 440 (2011) (Review) | (7) O. Tacar, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 65, 157 (2013) (Review) | (8) A.A. Wakharde, et al.; Am. J. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 1, 1009 (2018) (Review) | (9) X. Qiao, et al.; PNAS 117, 15182 (2020) (Review) | (10) H. Kumari, et al.; Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 7, 56 (2020) (Review)





