Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
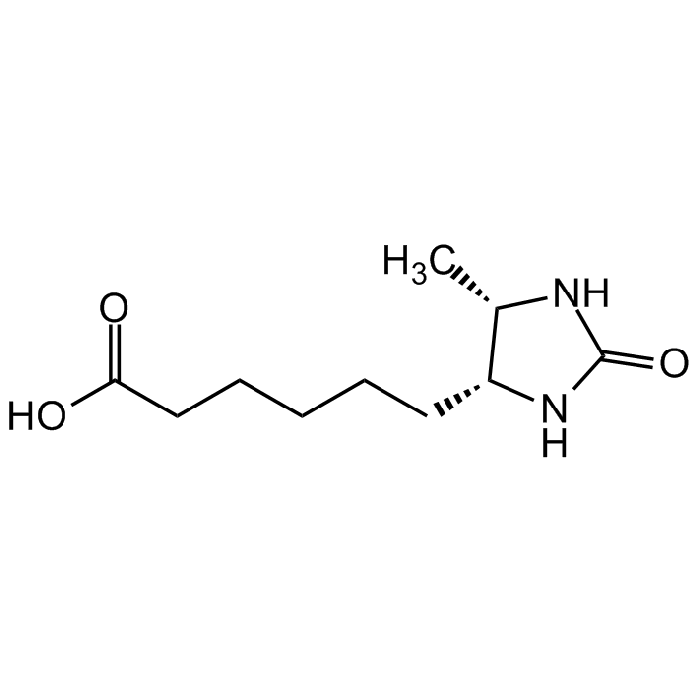
d-Desthiobiotin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 5-Methyl-2-oxo-4-imidazolidinehexanoic acid; Desthiobiotin |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C10H18N2O3 |
| MW | 214.26 |
| CAS | 533-48-2 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or DMF. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | AUTOLBMXDDTRRT-JGVFFNPUSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(O)CCCCC[C@H]([C@H](C)N1)NC1=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
D-Desthiobiotin is a protein cross-linking agent and a precursor in the synthesis of biotin. Desthiobiotin is a modified form of biotin that binds less tightly to avidin and streptavidin than biotin while still providing excellent specificity in affinity purification methods. Unlike biomolecules that are labeled with biotin, proteins and other targets that are labeled with desthiobiotin can be eluted without harsh, denaturing conditions. D-Desthiobiotin is used in affinity chromatography and protein chromatography, and can be used for protein and cell labeling, detection and isolation. It has been used in the preparation of agarose matrices for affinity-based isolation of streptavidin-fluorophore conjugates. Desthiobiotin is an efficient competitor for the mild elution of Strep-tag® and TwinStrep-tag® fusion proteins from Strep-Tactin® columns. For elution 2.5 mM desthiobiotin is added to the buffer.
(1) J.D. Hirsch, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 308, 343 (2002) | (2) R. Rodriguez-Melendez, et al.; J. Nutr. 133, 1259 (2003) | (3) S.C. Wu & S.L. Wong; Anal. Biochem. 331, 340 (2004) | (4) P. Guillaume, et al.; J. Immunol. 177, 3903 (2006) | (5) T.G.M. Schmidt, et al.; Protein Expr.Purif. 92, 54 (2013)





