Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
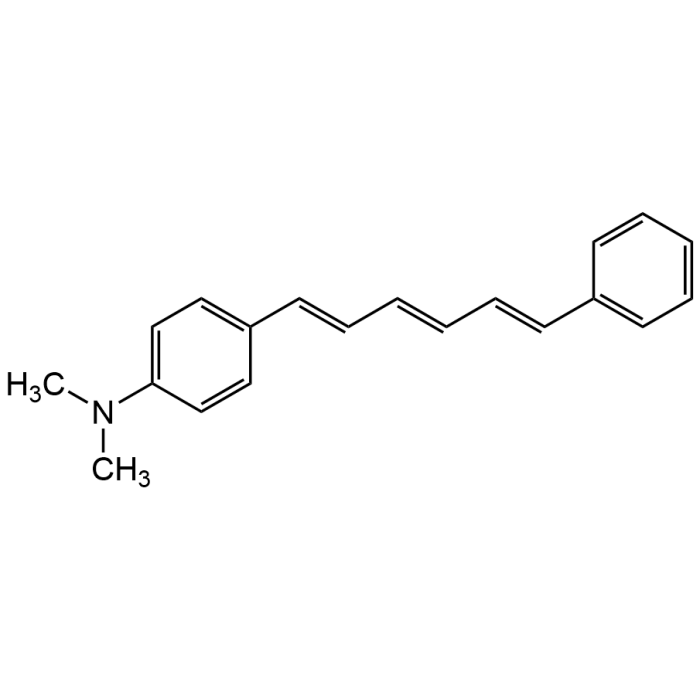
1-[4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl]-6-phenyl hexatriene
As low as
52
CHF
CHF 52.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-D0342-M0055 mgCHF 52.00
CDX-D0342-M02525 mgCHF 193.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DMA-DPH; 4′-(Dimethylamino)diphenylhexatriene |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C20H21N |
| MW | 275.39 |
| CAS | 79849-61-9 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥80% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol (1 mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | QNBRWGUCMQGGDA-YPXUENLVSA-N |
| Smiles | CN(C)C1=CC=C(/C=C/C=C/C=C/C2=CC=CC=C2)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
1-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-6-phenylhexa-1,3,5-triene (DMA-DPH) is a green-emitting dye that is part of a class of molecules known as "push-pull" chromophores. It can be used as a photoemitter in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) for screen displays and solid-state lighting applications. When dispersed in a polymer matrix, a mixture of neutral DMA-DPH (green emitter) and another chromophore can produce red, green, and blue light. The neutral form of DMA-DPH emits green light, while its protonated form, DMA-DPH_p, emits a high-intensity blue light, which is a key mechanism for producing blue color on demand. This makes DMA-DPH a versatile material for tuning emitted colors in OLEDs. DPH is used as a fluorescent probe to study cell membranes and lipid bilayers.
Product References
(1) F.W. Wang, et al.; Polymer 27, 1529 (1986) | (2) T. Suzuki & M. Kawakita; J. Biochem. 117, 881 (1995) | (3) M. Vasilopoulou, et al.; J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 10, 285 (2005) | (4) M. Vasilopoulou, et al.; Adv. Func. Mat. 17, 3477 (2007) | (5) I.S.K. Ioannis, et al.; Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 21273 (2011) | (6) S. Michlewska, et al.; Future Med. Chem. 11, 1741 (2019) | (7) A. Verykios, et al.; J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 55, 215106 (2022)





