Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
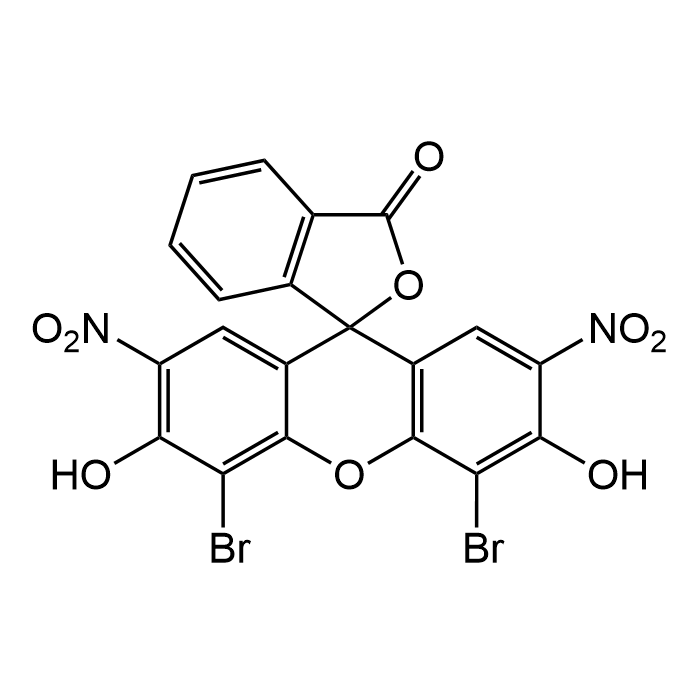
Eosin B
As low as
77
CHF
CHF 77.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-E0279-G02525 gCHF 77.00
CDX-E0279-G05050 gCHF 122.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 4′,5′-Dibromo-2′,7′-dinitrofluorescein; NSC 56650; Acid Red 91/C.I. 45400 (Sodium Salt form) |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C20H8Br2N2O9 |
| MW | 580.09 |
| CAS | 56360-46-4 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (Dye content UV/Vis) |
| Appearance | Orange to red powder or crystals. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water or ethanol. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ZBQZBWKNGDEDOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C2C(OC(C(Br)=C(O)C([N+]([O-])=O)=C3)=C3C24OC(C5=C4C=CC=C5)=O)=C1Br |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Eosin B is a xanthene-class acidic dye broadly used in histology, cytology and parasitology research for its staining properties and emerging pharmacological activity. In histology, Eosin B is used primarily as a counterstain for hematoxylin in methods like the H&E stain, differentiating between cell cytoplasm and nuclei by binding to positively charged components like proteins. Unlike the more common Eosin Y, Eosin B provides a distinctly bluish or bluish-purple hue to tissues rather than a yellowish one. It is used to stain cytoplasmic structures, connective tissues, and microorganisms, and is an integral part of the Romanowsky staining method. Beyond staining, more recent studies have revealed Eosin B’s potent antiparasitic/antimalarial effects, via a multifaceted mode of action involving enzyme inhibition (DHFR-TS, glutathione reductase, thioredoxin reductase), damage to parasite membranes and organelles, and possible redox cycling. Its differential toxicity, potent against parasites, much less against mammalian cells, makes it a promising lead for development of new antiparasitic agents. Spectral Data: λmax = 514nm (water, green fluorescence).
Product References
(1) A.A. Waheed & P.D. Gupta; Anal. Biochem. 233, 249 (1996) | (2) A.A. Waheed & P.D. Gupta; J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 33, 187 (1996) | (3) C.E. Atreya, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 278, 14092 (2003) | (4) K.M. Massimine, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 3132 (2006) | (5) X. Wang, et al.; Electrophoresis 31, 3808 (2010) | (6) M.Lai & B Lu; Compr. Sampl. Sample Prep. 3, 53 (2012) | (7) Z.X. Zhu, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 426, 1 (2012) | (8) Z. Zamani, et al.; Malar. Res. Treat. 2012, 381724 (2012) | (9) J.B. Fankam, et al.; Opt. Quant. Electr. 52, 292 (2020) | (10) M. Najafzadeh, et al.; Parasitol. Res. 121, 383 (2022)





