Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
Zin3 AM
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | FluoZin-3 AM (Registered Trademark of ThermoFisher) |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C46H44F2N2O20 |
| MW | 982.85 |
| CAS | 562102-46-9 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥85% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Orange to red solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or methanol. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | KMLHLVARODXKDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
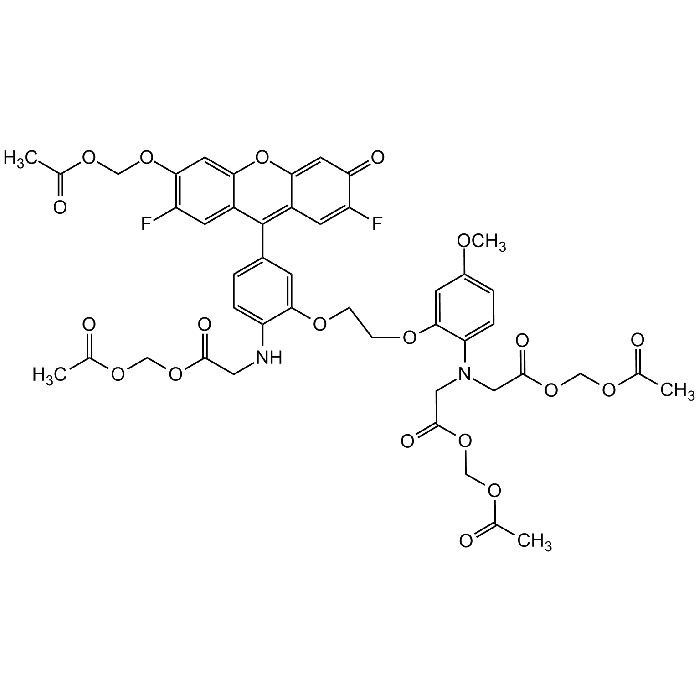
| Smiles | O=C1C(F)=CC2=C(C3=CC=C(NCC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)C(OCCOC4=CC(OC)=CC=C4N(CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)=C3)C5=CC(F)=C(OCOC(C)=O)C=C5OC2=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | -20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Zin3 AM is a cell-permeable Zn2+-selective indicator (Absorption=456nm), that once it enters the cell is hydrolized by esterases to convert the bright fluorescent Zin3 (Ex/Em: ~494/516nm). Zin3 is suitable for detection of Zn2+ concentrations in the 1–100 nM range and it has shown to be very Zn2+-sensitive and Zn2+-specific. The cell permeant AM-ester is useful for detecting low intracellular Zn2+ levels and small concentration changes. Zin3 exhibits high Zn2+-binding affinity that is unperturbed by Ca2+ concentrations up to at least 1 µM (Kd (Zn2+) (in buffer): ~15nM). In addition, Zin3 exhibits a >50-fold increase in fluorescence in response to saturating levels of Zn2+. This dye is usedpredominantly for imaging applications, but has also used in cell-based microplate assays and flow cytometry protocols. The product is typically loaded into cells by adding the dissolved indicator to medium containing cells.
Zinc is an important divalent cation in biological systems, influencing DNA synthesis, microtubule polymerization, gene expression, apoptosis, immune system function and the activity of enzymes such as carbonic anhydrase and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP). Zn2+ is also functionally active in synaptic transmission, and is a contributory factor in neurological disorders including epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease.
(1) K.R. Gee, et al.; Cell Calcium 31, 245 (2002) | (2) K.R. Gee, et al.; JACS 124, 776 (2002) | (3) W.J. Qian, et al.; Biotechniques 37, 922 (2004) | (4) M.J. Devinney, et al.; Cell Calcium 37, 225 (2005) | (5) F.A. Muylle, et al.; Biometals 19, 437 (2006) | (6) H. Haase, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 352, 222 (2006) | (7) Z.L. Datki, et al.; Brain Res. Bull. 74, 183 (2007) | (8) J. Zhao, et al.; Cell Calcium 44, 422 (2008) | (9) J. Zhao, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 384, 34 (2009) | (10) Y.M. Li, et al.; Cell Biochem. Funct. 27, 417 (2009) | (11) M.A. Namdarghanbari, et al.; J. Inorg. Biochem. 104, 224 (2010) | (12) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of biological dyes and stains (2010) | (13) I. Marszalek, et al.; J. Inorg. Biochem. 161, 107 (2016) | (14) I. Marszalek, et al.; Inorg. Chem. 57, 9826 (2019) | (15) L.M. Malaiyandi, et al.; Biometals (Epub ahead of print) (2019)













