Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
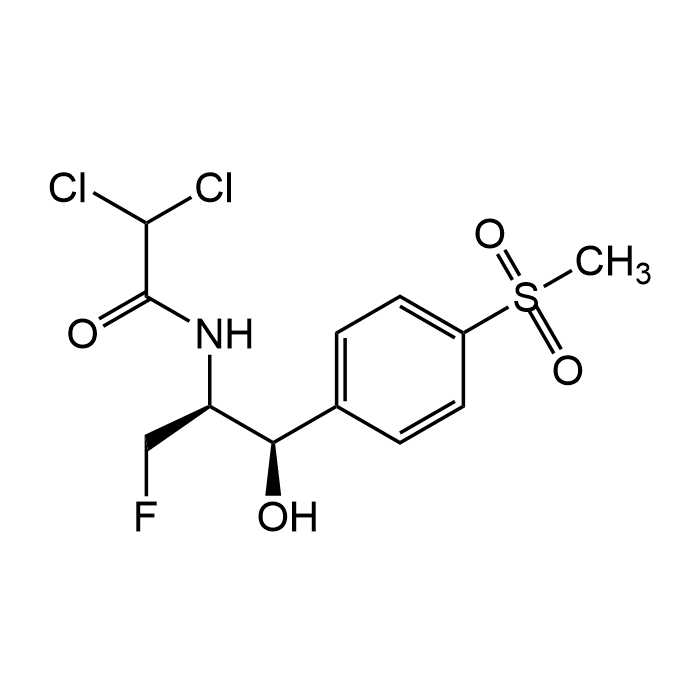
Florfenicol
As low as
206
CHF
CHF 206.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-F0069-G0055 gCHF 206.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Sch 25298; (-)-Florfenicol; Aquafen; 2,2-Dichloro-N-[(1S,2R)-1-(fluoromethyl)-2-hydroxy-2-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]ethyl]acetamide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C12H14Cl2FNO4S |
| MW | 358.21 |
| CAS | 73231-34-2 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (Assay) |
| Appearance | White to off white crystalline. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml), DMF (20mg/ml) or ethanol (10mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by IR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | AYIRNRDRBQJXIF-NXEZZACHSA-N |
| Smiles | [C@@H]([C@H](NC(C(Cl)Cl)=O)CF)(O)C1=CC=C(S(C)(=O)=O)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Florfenicol is a broad-spectrum fluorinated antibiotic and a derivative of thiamphenicol and analog of chloramphenicol. Florfenicol inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the A site of the 23S rRNA in the 50S subunit of the 70S ribosome, blocking peptidyl transferase activity, and thereby preventing peptide bond formation, which makes it effective against various bacteria. It is primarily used in veterinary medicine to treat respiratory infections in cattle and swine, and to prevent Salmonella infection in poultry. Although florfenicol is primarily known for its antimicrobial activity, it also shows immunomodulatory properties, including anti-inflammatory activity, downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, suppression of innate immune responses, affect lymphocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin production, and influence TLR expression in immune cells.
Product References
(1) H.C. Neu & K.P. Fu; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 18, 311 (1980) | (2) V.P. Syriopoulou, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 19, 294 (1981) | (3) R. Graham, et al.; Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 7, 691 (1988) | (4) M. Cannon, et al.; J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 26, 307 (1990) | (5) Y. Ueda & I. Suenaga; J. Vet. Med. Sci. 57, 363 (1995) | (6) S. Priebe & S. Schwarz; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 2703 (2003) | (7) G. Shuang, et al.; Immunol. Invest. 40, 356 (2011) | (8) X. Guo, et al.; Environ. Res. 244, 117934 (2024) (Review)





