Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
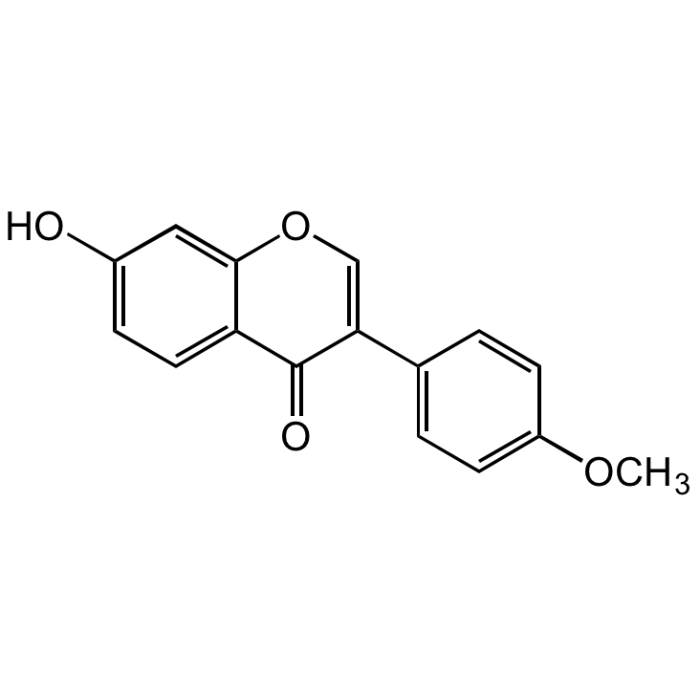
Formononetin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Biochanin B; NSC 93360; 7-Hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; 7-Hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromone, 7-Hydroxy-4'-methoxyisoflavone |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C16H12O4 |
| MW | 268.26 |
| CAS | 485-72-3 |
| RTECS | DJ3100114 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml), DMF (30mg/ml) or ethanol (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | HKQYGTCOTHHOMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=CC=C(C(C(C2=CC=C(OC)C=C2)=CO3)=O)C3=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Formononetin is an isoflavonoid phytoestrogenic compound found in soy-based foods and is the precursor of daidzein. It acts as an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and a selective inhibitor of ADH γ (the γ-isoform of alcohol dehydrogenase). It displays potent antitumor, antiviral, anti-inflammatory (inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome), antioxidant, neuroprotective and neuroinflammatory properties. Also shown to have vasorelaxant, antihypertensive and antihyperglycemic (AMPK activator) properties. Induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in several cancer cells in vitro and in vivo and shows anti-angiogenic (FGFR2 inhibitor), anti-invasive and anti-migratory effects. Increases adipocyte thermogenesis by modulating PPARγ activity. Shown to promote early fracture healing through stimulating angiogenesis by up-regulating VEGFR-2/Flk-1 and endothelial repair and wound healing in a process involving the over-expression of Egr-1 transcription factor through the regulation of the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways.
Binding to human cell-surface receptor HSPA5 and prevents SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from binding to HSPA5 SBDβ in silico.
(1) W.M. Keung; BBRC 215, 1137 (1995) | (2) S. Toda and Y. Shirataki; Phytother. Res. 13, 163 (1999) | (3) C.K. Wong & W.M. Keung; J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 71, 191 (1999) | (4) B.L. Pool-Zobel, et al.; Carcinogenesis 21, 1247 (2000) | (5) S. Medjakovic & A. Jungbauer ; J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol 108, 171 (2008) | (6) H. Mu, et al.; Phytomedicine 16, 314 (2009) | (7) J.E . Huh, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 9, 1357 (2009) | (8) J.E . Huh, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 11, 46 (2011) | (9) T. Sun, et al.; Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 32, 1009 (2011) | (10) J. Chen, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 43, 681 (2011) | (11) M. Sun, et al.; J. Alzheimers Dis. 28, 795 (2012) | (12) Y. Ye, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 44, 263 (2012) | (13) K.K. Auyeung, et al.; Oncol. Rep. 28, 2188 (2012) | (14) R. Zhou, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 46, 753 (2014) | (15) Y. Yang, et al.; Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 7, 8453 (2014) | (16) X.Y. Wu, et al.; Oncotarget 6, 44563 (2015) | (17) H. Wang, et al.; Virol. J. 12, 1 (2015) | (18) G. Qiu, et al.; Exp. Biol. Med. 242, 223 (2017) | (19) J. Gautam, et al.; Br. J. Nutr. 117, 645 (2017) | (20) T. Nie, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 175, 1439 (2018) | (21) D. Wu, et al.; Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 3048532 (2018) | (22) A. El-Bakoush & O.A. Olajide; Int. Immunopharmacol. 61, 325 (2018)
Natural products may interfere with SARS-CoV-2 attachment to the host cell: A.A. Elfiky, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1 (2020)





