Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
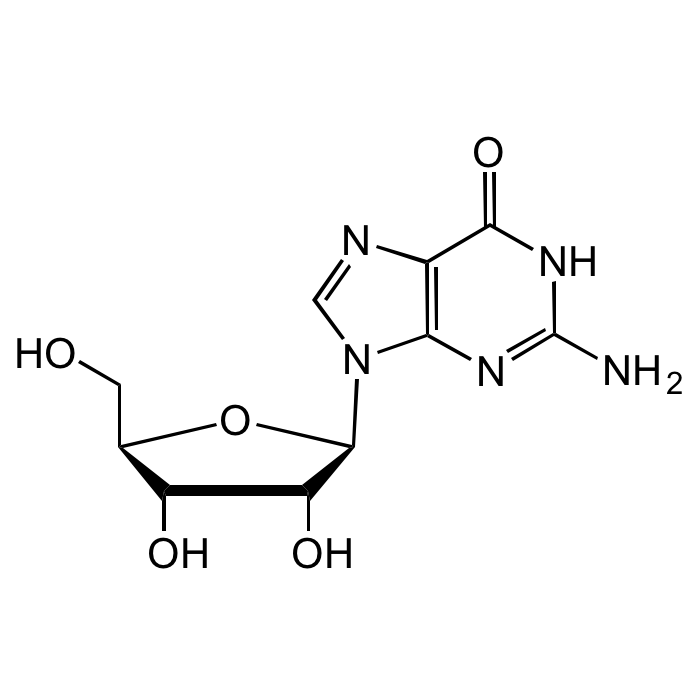
Guanosine
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 9-β-D-Ribofuranosyl-guanine; Guanine-9-β-D-ribofuranoside; 2-Amino-β-D-ribofuranosyl-9H-purine-6-(1H)-one |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C10H13N5O5 |
| MW | 283.24 |
| CAS | 118-00-3 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to light yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in formic acid:water (1:1) (~50mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UUOKFMHZSA-N |
| Smiles | O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](N2C(N=C(N)NC3=O)=C3N=C2)O[C@@H]1CO |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). Guanosine has important functions in cell metabolism and a protective role in response to degenerative diseases or injury with neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects. Required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA message by cutting at both ends, re-ligating, and leaving just the exons on either side to be translated into protein.
(1) M. Rathbone, et al.; Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 27, 666 (2008) | (2) D. Lanznaster, et al.; Aging Dis. 7, 657 (2016)





