Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
Gram's fuchsin Solution
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Fuchsin solution; Basic Red 9; Magenta O; Basic Violet 14 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
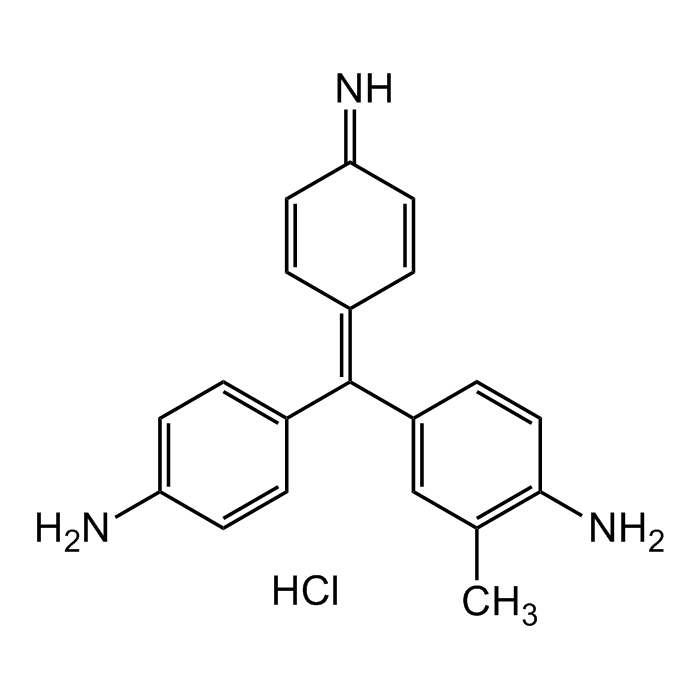
C20H20ClN3 |
| MW | 337.85 |
| CAS | 632-99-5 |
| RTECS | CX9850000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Dark red liquid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by UV/Vis. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | NIKFYOSELWJIOF-SVFFXJIWSA-N |
| Smiles | NC1=CC=C(/C(C2=CC(C)=C(N)C=C2)=C3C=CC(C=C/3)=N)C=C1.Cl |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Gram's Fuchsin Solution is a reagent that could be used in qualitative procedures to differentiate gram-negative from gram-positive organisms. The Gram staining allows a fast differentiation of bacteria in Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The mureine structure of the bacteria walls is the basis of the color affinity. Bacteria will be stained with Gram's crystal violet solution - an aniline dye - in the first step. After the treatment with iod solution, a dye-iod complex will form. During the decolorizing step, this complex stays in the multilayer mureine structures of the Gram-positive bacteria and they will appear blue/violet. Gram-negative bacteria have a monolayer mureine structure only, the dye-iod complex does not stay bound to the cellwall, they will be decolorized. Gram-negative bacteria will be counterstained by Gram's Fuchsin solution and appear red/pink. Both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria pick up the counterstain. The counterstain, however, is unseen on Gram-positive bacteria because of the darker crystal violet stain.
(1) E. Adams; Stain Technol. 50, 227 (1975) | (2) T.J. Beveridge; Biotech. Histochem. 76, 111 (2001) | (3) R. Coico, et al.; Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. Appendix 3-3C (2005)





