Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
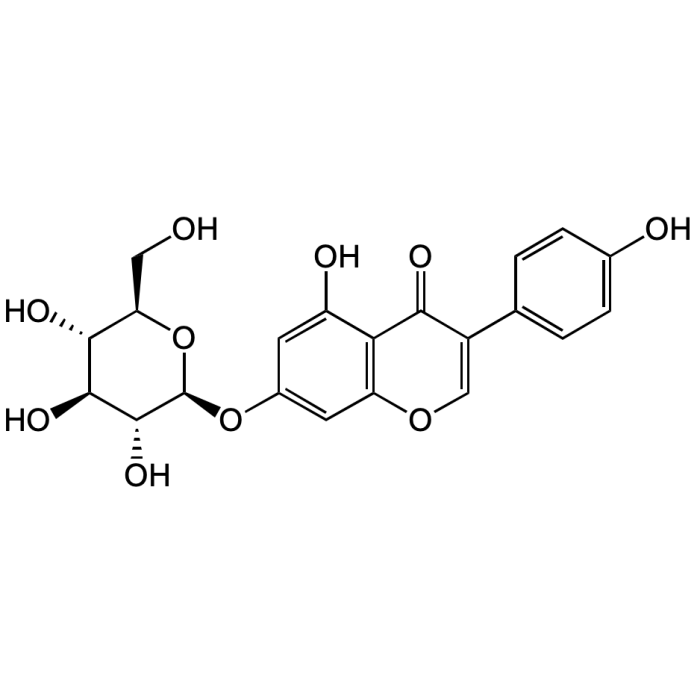
Genistin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Genistein glycoside; NSC 5112; 4',5,7-Trihydroxyisoflavone 7-glucoside |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C21H20O10 |
| MW | 432.38 |
| CAS | 529-59-9 |
| RTECS | DJ3093000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from plant source. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Light-Yellow Powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or DMF (10mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ZCOLJUOHXJRHDI-CMWLGVBASA-N |
| Smiles | OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](OC2=CC(OC=C(C3=CC=C(O)C=C3)C4=O)=C4C(O)=C2)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Genistin is a natural isoflavone glycoside isolated from legumes (e.g. soy). It is a selective inhibitor of mammalian terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl-transferase (TdT), with no measurable effect on mammalian or microbial DNA polymerases. Disrupts cell cycle and induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer SK-OV-3 cells. Inhibits UV light-induced plasmid DNA damage and cell growth in human melanoma cells. It is a phytoestrogen, as it stimulates the growth of estrogen-dependent human breast cancer cells in vivo. Like other isoflavones, genistin promotes the proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts and suppresses bone turnover. It also increases bone formation in collagen matrix in vivo. Could also be used as a negative control for the PTK inhibitor Genistein.
(1) C.D. Allred, et al.; Carcinogenesis 22, 1667 (2001) | (2) T. Uesugi, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 24, 368 (2001) | (3) Y. Uchiyama, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1725, 298 (2005) | (4) A. Russo, et al.; J. Nutr. Biochem. 17, 103 (2006) | (5) E.J. Choi, et al.; Life Sci. 80, 1403 (2007) | (6) R.W. Wong & A.B. Rabie; Front. Biosci. 2, 764 (2010)





