Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
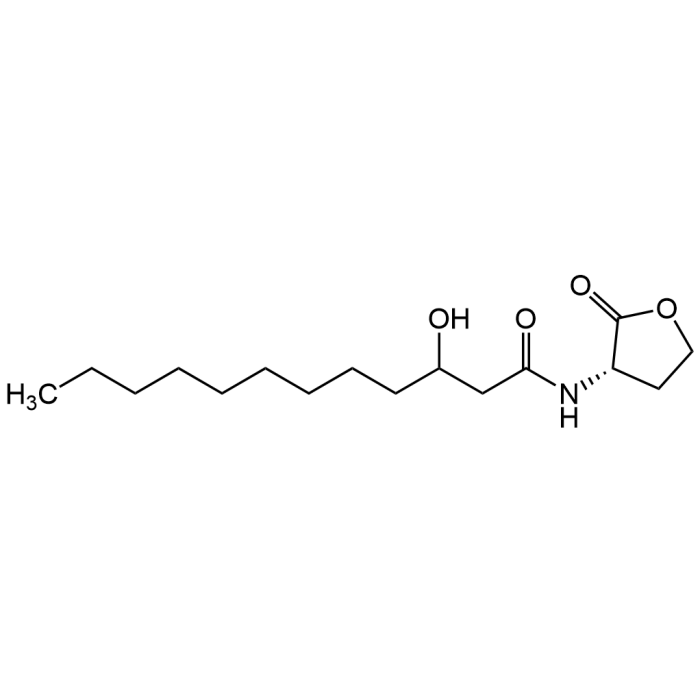
N-(3-Hydroxydodecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3OH-C12-HSL; 3-Hydroxy-N-(tetrahydro-2-oxo-3-furanyl)dodecanamide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C16H29NO4 |
| MW | 299.41 |
| CAS | 216596-73-5 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMF, acetonitrile or chloroform. Ethanol or methanol are not recommended as solvents as they have been shown to open the lactone ring. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | RGTXFFYJJNWEPV-KZUDCZAMSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(CC(CCCCCCCCC)O)N[C@@H]1C(OCC1)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Quorum sensing agent. N-(3-Hydroxydodecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (3OH-C12-HSL) is a small diffusible signaling molecule and is a member of N-acyl-homoserine lactone family. N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHL) are involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism. The diverse applications of this kind of molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention and formation of biofilms. The DL-version of 3OH-C12-HSL, triggered apoptosis of bone marrow-derived macrophages through ER- and mitochondria-mediated pathways and as a virulence factor, contributed to bacterial infection and survival as well as the modification of host responses in the early stages of infection [6].
(1) S.R. Chhabra, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 46, 97 (2003) | (2) C.L. Weingart, et al.; Mol. Microbiol. 57, 452 (2005) | (3) P. Lumjiaktase, et al.; Microbiol. 152, 3651 (2006) | (4) A. Gonzalez, et al.; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 3729 (2013) | (5) E. Readel, et al.; Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 412, 2927 (2020) | (6) K. Woo, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 7565 (2021)





