Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
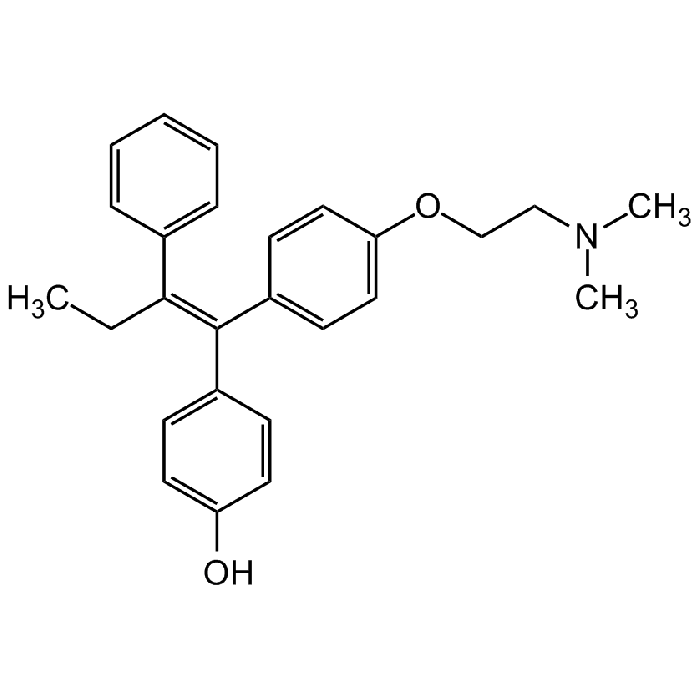
4-Hydroxytamoxifen
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Afimoxifene; 4-OHT; cis/trans-4-Hydroxytamoxifen; (E/Z)-4-Hydroxytamoxifen; HTMX; 4-(1-[4-(Dimethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]-2-phenyl-1-butenyl)phenol |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C26H29NO2 |
| MW | 387.51 |
| CAS | 68392-35-8 |
| RTECS | SL1210000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol or methanol (both 5mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | TXUZVZSFRXZGTL-QPLCGJKRSA-N |
| Smiles | CC/C(C1=CC=CC=C1)=C(C2=CC=C(O)C=C2)/C3=CC=C(OCCN(C)C)C=C3 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an active metabolite of the chemotherapeutic drug tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that acts as an agonist or antagonist in various tissues. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen acts as a tissue-selective agonist-antagonist of the estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen is an isoform-specific inhibitor of orphan estrogen-receptor-related (ERR) nuclear receptors β and γ. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen exhibits anticancer chemotherapeutic activity, inducing autophagy and vacuole formation as well as KRAS degradation in various cancer cell lines. In cardiac myocytes, 4-hydroxytamoxifen decreases Ca2+ amplitude, slowing relaxation and decreasing contractility. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen has also shown to be a potent inhibitor of the mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT).
[1] N. Terakawa, et al.; Cancer 61, 1312 (1988) | [2] H. Wiseman, et al.; FEBS Lett. 274, 107 (1990) | [3] G. Freiss, et al.; BBRC 173, 919 (1990) | [4] H. Wiseman, et al.; Biochem J. 292, 635 (1993) | [5] A.M. Davies, et al.; Biochem. Soc. Trans. 23, 439S (1995) | [6] S.T. Willard, et al.; Endocrine 14, 247 (2001) | [7] P. Coward, et al.; PNAS 98, 8880 (2001) | [8] G.B. Tremblay, et al.; Endocrinology 142, 4572 (2001) | [9] H.K. Crewe, et al.; Drug Metab. Dispos. 30, 869 (2002) | [10] C.M. Cardoso, et al.; Mitochondrion 1, 485 (2002) | [11] J.P. Monteiro, et al.; Toxicol. In Vitro 17, 629 (2003) | [12] Z. Desta, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 310, 1062 (2004) | [13] H. Seeger, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 36, 277 (2004) | [14] E.A. Ariazi & V.C. Jordan; Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 6, 203 (2006) (Review) | [15] M.L. Asp, et al.; PLoS One 8, e78768 (2013) | [16] L. Kohli, et al.; Cancer Res. 73, 4395 (2013) | [17] L. Duan, et al.; Cancer Lett. 353, 290 (2014)





