Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
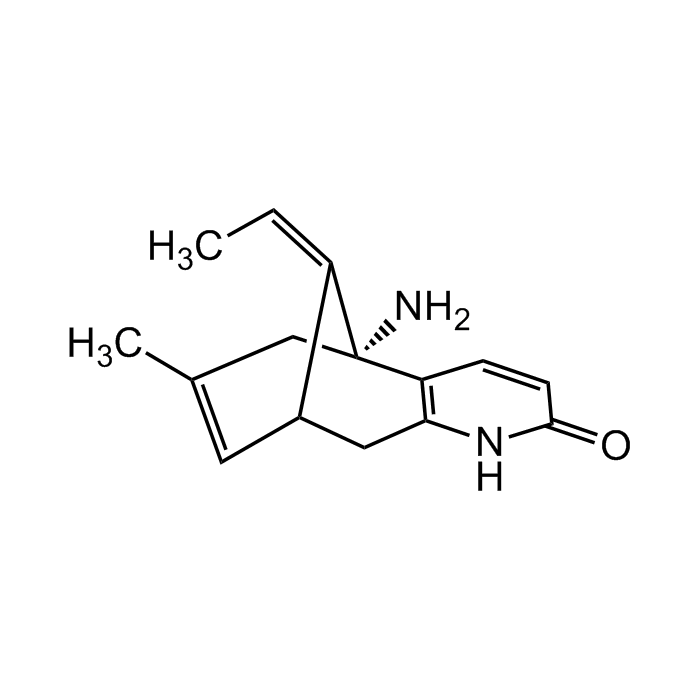
(-)-Huperzine A
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Hup A; (-)-Selagine; Kimpukan A |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H18N2O |
| MW | 242.32 |
| CAS | 102518-79-6 |
| RTECS | PB9185700 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or methanol (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ZRJBHWIHUMBLCN-ZUZCIYMTSA-N |
| Smiles | C/C=C1[C@@H]2CC3=C(C=CC(N3)=O)[C@@]/1(N)CC(C)=C2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Huperzine A is a natural sesquiterpene alkaloid. It showns neuroprotective activity. It is a potent acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor and displays oral AChE inhibitory activity in animals. Huperzine A has potential applications in a variety of neuroprotective roles, including protection against organophosphate nerve agents and ameliorating symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. It has been shown to reduce neuronal cell death caused by glutamate and to have anti-inflammatory effects. It also has been shown to be an antagonist of NMDA receptor in cerebral cortex. It has been shown to ameliorate cognitive deficits.
(1) S.J. Geib, et al.; Acta Crystallogr. C. 47, 824 (1991) | (1) H.S. Ved, et al.; Neuroreport 8, 963 (1997) | (1) J.M. Zhang & G.Y. Hu; Neuroscience 105, 663 (2001) | (1) R.K. Gordon, et al.; J. Appl. Toxicol. 21, S47 (2001) | (1) J. Zhou & X.C. Tang; FEBS Lett. 526, 21 (2002) | (1) R. Wang & X.C. Tang; Neurosignals 14, 71 (2005) (Review) | (1) H.Y. Zhang X.C. Tang; Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 27, 619 (2006) (Review) | (1) Z.F. Wang, et al.; J. Neurochem. 106, 1594 (2008) | (1) X.Y. Mao, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 7667 (2014) | (1) H.Y. Zhang, et al.; Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 28, 173 (2008) (Review) | (1) U. Damar, et al.; Expert Rev. Neurother. 16, 671 (2016) (Review)





