Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
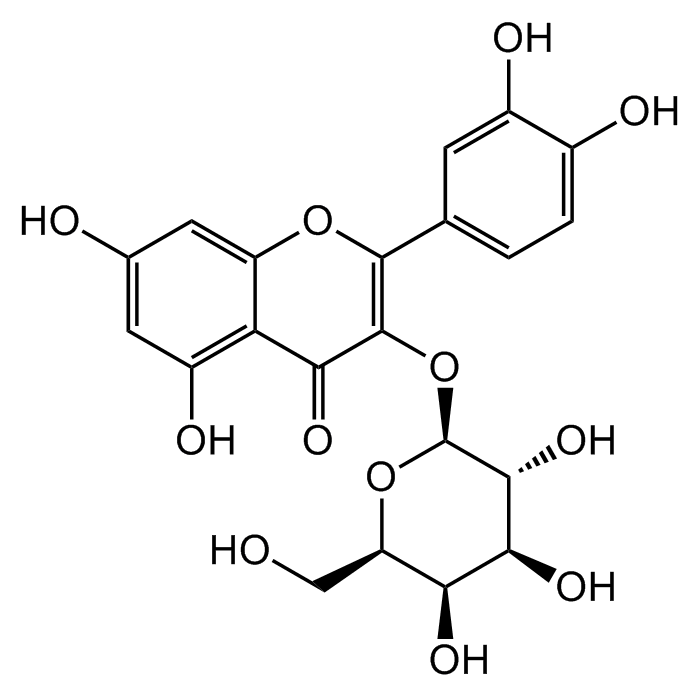
Hyperoside
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3,3',4',5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone 3-D-galactoside; Hyperin; Quercetin 3-D-galactoside; NSC 407304 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C21H20O12 |
| MW | 464.38 |
| CAS | 482-36-0 |
| RTECS | DJ3009200 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or DMF (10mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | OVSQVDMCBVZWGM-DTGCRPNFSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1C2=C(O)C=C(O)C=C2OC(C3=CC=C(O)C(O)=C3)=C1O[C@@H]4O[C@H](CO)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]4O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Hyperoside is a 3-O-galactoside of quercetin that can be found in a wide range of plants. It shows diverse biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antihypoglycemic and antiadipogenic, antibacterial and anticancer properties. It has powerful antioxidant action through its ability to scavenge free radicals. It inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway. Hyperoside selectively interrupted NLRC4 and AIM2 inflammasome activation but did not alter cytokine expression. The quorum sensing-inhibiting effect of hyperoside may lead to a reduction in biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa. Honokiol exerts broad-range anticancer activity, such as induction of apoptosis and autophagy and inhibition of cell proliferation. Hyperoside has a beneficial effect on the prevention and treatment of obesity.
(1) M.J. Piao, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1780, 1448 (2008) | (2) S.J. Kim, et al.; Am. J. Chin. Med. 39, 171 (2011) | (3) K.W. Zeng, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 672, 45 (2011) | (4) N. Zhang, et al.; PLoS One 9, e98973 (2014) | (5) S.K. Ku, et al.; Inflammation 38, 784 (2015) | (6) T. Fu, et al.; Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 37, 505 (2016) | (7) P. Lu; Biomed. Pharmacother. 82, 216 (2016) | (8) H. Ahn & G.S. Lee; Phytomedicine 24, 77 (2017) | (9) Y. Sun, et al.; Exp. Ther. Med. 14, 1647 (2017) | (10) Y. Zhang, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Med. 41, 77 (2018) | (11) M. Berkoz; Acta Endocrinol. 15, 165 (2019)





