Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
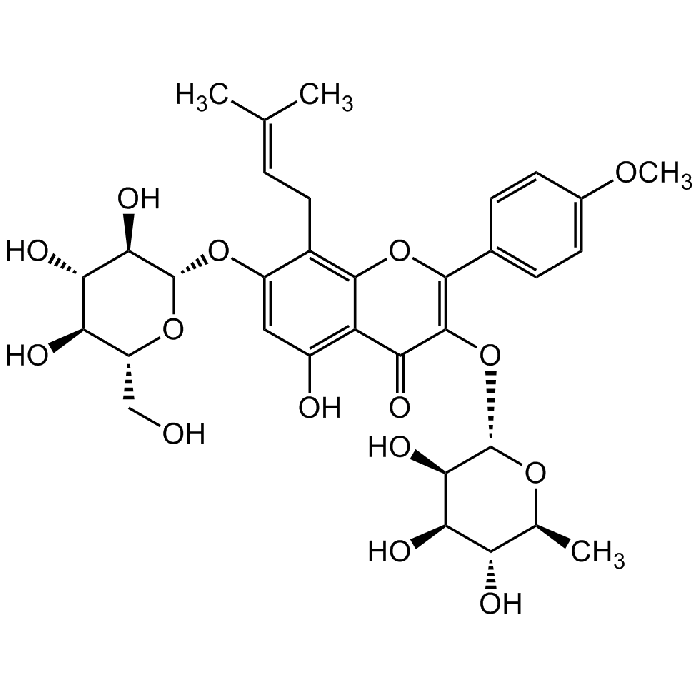
Icariin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 4'-O-Methyl-8-γ,γ-dimethylallylkaempferol-3-rhamnoside-7-glucoside; Leariline |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C33H40O15 |
| MW | 676.668 |
| CAS | 489-32-7 |
| RTECS | DJ2980500 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Light yellow fine powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or DMF (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | TZJALUIVHRYQQB-XLRXWWTNSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1C2=C(O)C=C(O[C@H]3[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O3)C(C/C=C(C)/C)=C2OC(C4=CC=C(OC)C=C4)=C1O[C@H]5[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)O5 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Icariin, the active component of the Chinese medicinal plant E. brevicornum. It has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidant, osteoprotective, neuroprotective and cardioprotective activity. It has been shown to enhance bone formation and bone regeneration. Icariin may be beneficial to Alzheimer's disease by reducing the production of extracellular amyloid plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles and inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 activity. The anti-cancer activity is related to various mechanisms such as apoptosis and autophagy induction, cell cycle modulation, antiangiogenesis and antimetastasis, modulating multidrug resistance and immunomodulation. Icariin interacts with several pathways, like PDE, TGF-β, MAPK, PPAR, NOS, IGF, Sirtuin and others. Icariin has been shown to inhibit the NF-κ activation pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome.
(1) L.G. Ming, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 228, 513 (2013) (Review) | (2) J.K. Schluesener & H. Schluesener; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 58, 49 (2014) (Review) | (3) H.L. Tan, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 7, 191 (2016 (Review) | (4) R. Shen & J.H. Wang; Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 7, 50 (2018) (Review) | (5) B. Su, et al.; Life Sci. 208, 26 (2018) | (6) J. Jin, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 842, 20 (2019) (Review) | (7) C. Angeloni, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 10, 271 (2019) (Review) | (8) A. Yang, et al.; Stem Cells Int. 2019, 5747298 (2019) (Review)





