Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
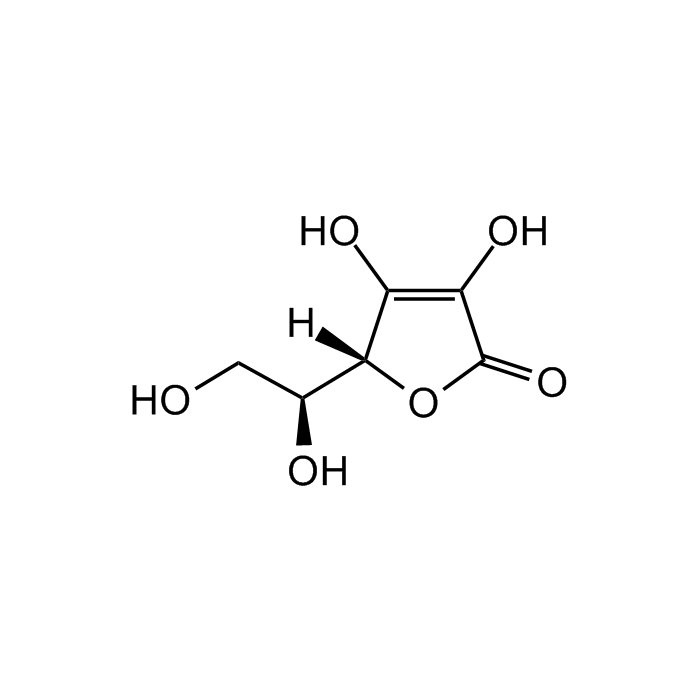
L-Ascorbic acid
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | L-Threoascorbic acid; Antiscorbutic factor; Vitamin C; Ascorbate; NSC 33832; NSC 218455 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C6H8O6 |
| MW | 176.12 |
| CAS | 50-81-7 |
| RTECS | CI7650000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (Assay) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (50mg/ml) or DMSO (10mg/ml) . |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=C(O)[C@]([C@@H](O)CO)([H])OC1=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
L-Ascorbic acid (better known as Vitamin C) is a naturally occurring electron donor and therefore serves as a reducing agent. It is synthesized from glucose in the liver of most mammalian species, excluding humans, non-human primates, or guinea pigs who must obtain it through dietary consumption. In humans, L-Ascorbic acid acts as an electron donor for eight different enzymes, including those related to collagen hydroxylation, carnitine synthesis (which aids in the generation of adenosine triphosphate), norepinephrine synthesis, tyrosine metabolism and amidating peptides. L-Ascorbic acid demonstrates antioxidant activity that may be of some benefit for reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and cataracts. L-Ascorbic acid is an inhibitor of Cav3.2 channels, but displays no effect on Cav3.1 or Cav3.3 channels heterologously expressed in HEK 293 cells. L-Ascorbic acid enhances the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from mouse and human somatic cells by increasing reprogramming efficiency. It is also a commonly used antifade reagent in live cell microscopy. Ascorbate has critical roles in the central nervous system (CNS); it is a neuromodulator of glutamatergic, cholinergic, dopaminergic and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic neurotransmission, provides support and structure to neurons, and participates in processes such as differentiation, maturation and survival of neurons. L-Ascorbic acid is essential to stimulate the immune system. Its immunostimulant, anti-inflammatory, antiviral and antibacterial properties are well known. Due to its effects and diversity of regulated pathways, L-Ascorbic acid is suitable for use in various fields of medicine including immunology, toxicology, radiobiology and is co-applied as an adjuvant to regulate immunity, gene expression and other important physiological processes.
(1) S. Englard & S. Seifter; Ann. Rev. Nutr. 6, 365 (1986) (Review) | (2) B. Peterkofsky; Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54, 1135S (1991) | (3) C.J. Rebouche; Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54, 1147S (1991) | (4) E.J. Diliberto, et al.; Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54, 1163S (1991) | (5) S.J. Padayatty, et al.; J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 22, 18 (2003) | (6) S.S. Gropper, et al.; Adv. Nutr. Human Metab. 4, 259 (2005) | (7) M.T. Nelson, et al.; J. Neurosci. 27, 12577 (2007) | (8) M.A. Esteban, et al.; Cell Stem Cell 6, 71 (2010) | (9) T. Cordes, et al.; Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 6699 (2011) | (10) A. Sorice, et al.; Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 14, 444 (2014) (Review) | (11) M. Moretti, et al.; CNS Drugs 31, 571 (2017) (Review) | (12) R. Bakalova, et al.; Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 1504048 (2020) (Review) | (13) D. Njus, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 159, 37 (2020) (Review)





