Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
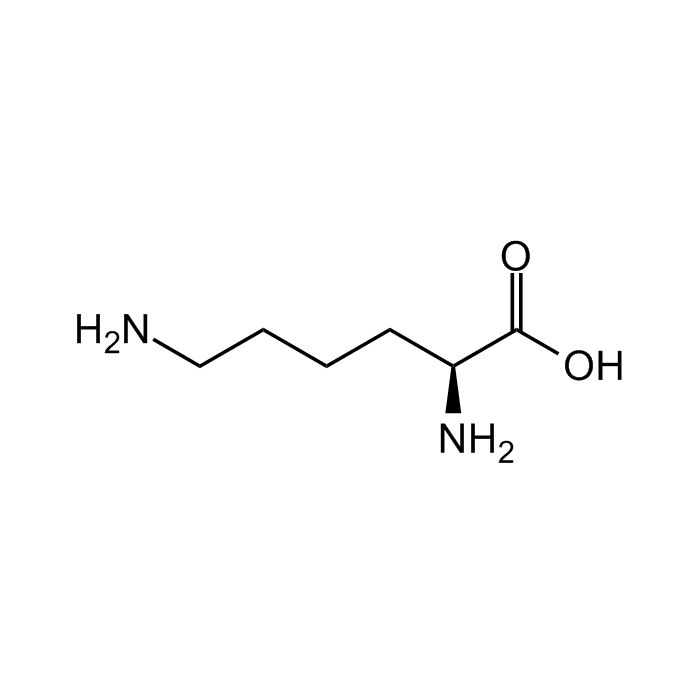
L-Lysine
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | H-Lys-OH; (S)-Lysine; (S)-2,6-Diaminocaproic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C6H14N2O2 |
| MW | 146.19 |
| CAS | 56-87-1 |
| RTECS | OL5540000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Fermented from plant source. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (TLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N |
| Smiles | NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep under inert gas. Very hygroscopic. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
L-Lysine is an essential α-amino acid, which is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. It is a key building block in protein synthesis in which it acts as a base. Lysine residues are useful in many cellular processes, due to their ability to accept a wide variety of post-translational modifications. These modifications include acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, neddylation, biotinylation, pupylation and carboxylation. L-lysine is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by humans and mammals through transamination. Lysine plays a pivotal role in different processes inside the human body, such as proteinogenesis, catalysis, fatty acid metabolism, histone modification, polypeptide crosslinking, calcium homeostasis, and acts as a nucleophile in enzymatic reactions. Because of its pivotal role in promoting growth and development, enhancing immunity, and preventing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, L-lysine is used in food health care, feed additives and pharmaceutical preparations.
(1) M. Smriga & K. Torii; PNAS 100, 15370 (2003) | (2) L. Tosha, al.: Biochem. J. 435, 509 (2011) | (3) F.-M. Boisvert, et al.; Mol. Cell Proteomics 11, M111.011429 (2012) | (4) F.K.D.C Felix, et al.; Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 39, 1031 (2019) | (5) K. Hayamizu, et al.; J. Nutr. 150, 2561S (2020) | (6) D. Zhang, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 3189 (2021) | (7) Q. Li, et al.; Molecules 27, 35209157 (2022) | (8) S. Muduli, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. acta 1867, 130320 (2023)





