Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
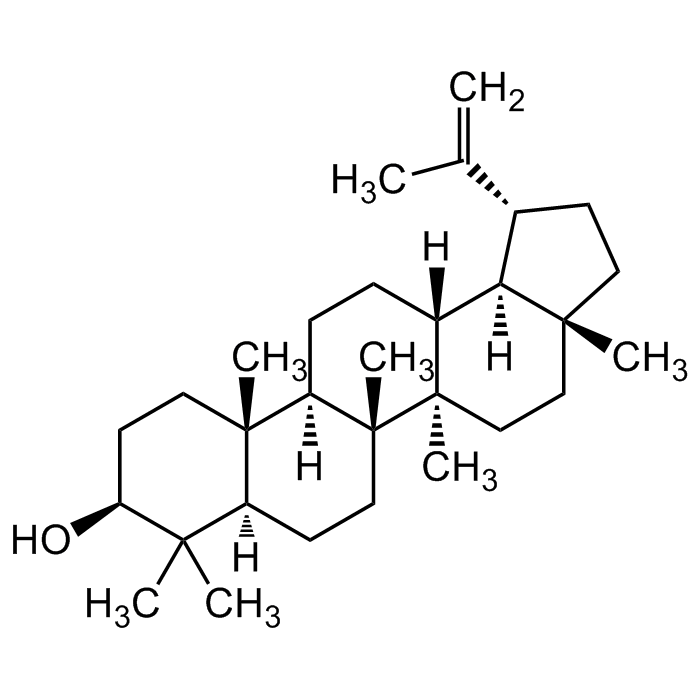
Lupeol
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | β-Viscol; 20(29)-Lupen-3β-ol; 3β-Hydroxy-20(29)-lupene; Clerodol; Fagarasterol; Lupenol; Monogynol B; NSC 90487 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C30H50O |
| MW | 426.72 |
| CAS | 545-47-1 |
| RTECS | OK5763000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White Powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (1mg/ml), DMF (1mg/ml) or ethanol (1mg/ml). Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | MQYXUWHLBZFQQO-QGTGJCAVSA-N |
| Smiles | C[C@@]12CC[C@@]3(C)[C@]4(C)CC[C@@]5([H])C(C)(C)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]5(C)[C@@]4([H])CC[C@]3([H])[C@@]1([H])[C@H](C(C)=C)CC2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Lupeol, is a dietary triterpene found in certain fruits, vegetables, and medicinal plants. Lupeol has been shown tohave a broad range of activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antihyperglycemic, antidyslipidemic, antimutagenic, anti-diabetic, anti-asthma, antiprotozoal, antimicrobial, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective and neuroprotective properties. It is a multi-target agent targeting proteins such as α-glucosidase, α-amylase, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP 1B) and TCA cycle enzymes and targeting pathways such as IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-mediated toll-like receptor 4 (IRAK-TLR4), Bcl-2 family, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κ), phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3-K)/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways.
(1) S. Sunitha, et al.; Fitoterapia 72, 516 (2001) | (2) M.A. Fernandez, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 53, 1533 (2001) | (3) Y.J. You, et al.; Phytother. Res. 17, 341 (2003) | (4) M. Saleem, e al.; Oncogene 23, 5203 (2004) | (5) J. Fotie, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 69, 62 (2006) | (6) M. Saleem, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 2119 (2008) | (7) M. Saleem, et al.; Carcinogenesis 30, 808 (2009) | (8) K. Papi Reddy, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19, 4463 (2009) | (9) R.S. Tarapore, et al.; Carcinogenesis 31, 1844 (2010) | (10) H.R. Siddique, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 5379 (2011) | (11) H.R. Siddique & M. Saleem; Life Sci. 88, 285 (2011) (Review) | (12) F.S. Tsai, et al.; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 929, 145 (2016) (Review) | (13) V.R. Machado, et al.; Nat. Prod. Res. 32, 275 (2018) | (14) A. Malik, et al.; Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 13, 1501 (2019)





