Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
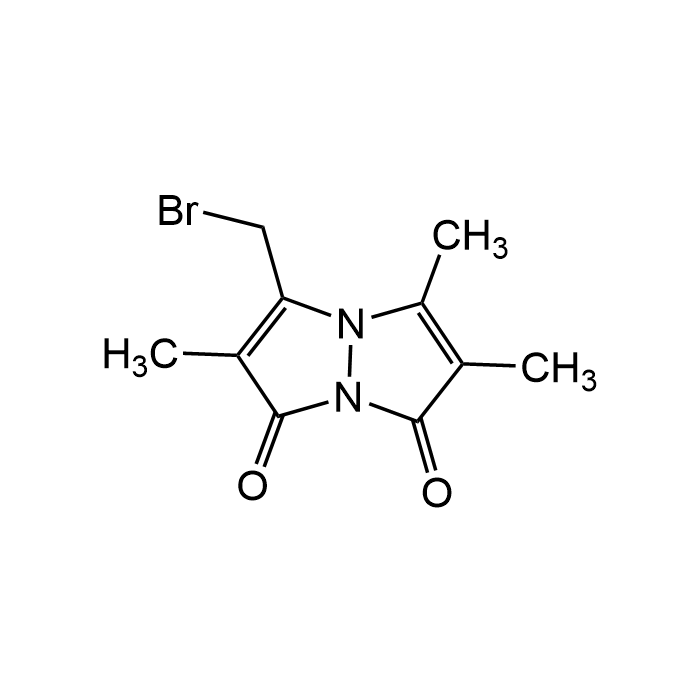
Monobromobimane
As low as
103
CHF
CHF 103.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-M0061-M02525 mgCHF 103.00
CDX-M0061-M100100 mgCHF 348.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Bromobimane; mBBr; Monobrombiman; Thiolyte MB; NSC 608544 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C10H11BrN2O2 |
| MW | 271.11 |
| CAS | 71418-44-5 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml) or DMF (30mg/ml). Slightly soluble in ethanol (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | AHEWZZJEDQVLOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | BrCC1=C(C)C(N2N1C(C)=C(C)C2=O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Monobromobimane (mBBr) is the most popular thiol-reactive fluorogenic probe. While bromobimane itself is essentially nonfluorescent, it alkylates thiol groups, displacing the bromine and adding the fluorescent tag to the thiol. It is cell-permeable, reacts rapidly at physiological pH with available thiol groups, and generates a stable fluorescent signal. Monobromobimane can be used to evaluate or quantify a variety of compounds containing reactive sulfur or thiol groups, including H2S, glutathione, proteins, and nucleotides. The absorption and emission maxima for monobromobimane are 398 and 490 nm, respectively. mBBr is commonly applied in redox biology research to monitor intracellular thiol status, oxidative stress, and antioxidant capacity, as well as in enzymatic activity assays involving thiol-containing proteins.
Product References
(1) N.S. Kosower, et al.; PNAS 76, 3382 (1979) | (2) H. Gainer & N.S. Kosower; Histochem. 68, 309 (1980) | (3) G.L. Newton, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 114, 383 (1981) | (4) P.B. Hubert & S.I. Yakubu; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 35, 384 (1983) | (5) G.C. Rice, et al.; Cancer Res. 46, 6105 (1986) | (6) P.C. Chinn, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 159, 143 (1986) | (7) I.A. Cotgreave & P. Moldeus; J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 13, 231 (1986) | (8) R.C. Fahey & G.L. Newton; Methods Enzymol. 143, 85 (1987) | (9) E.M. Kosower & N.S. Kosower; Methods Enzymol. 251, 133 (1995) | (10) G.L. Newton & R.C. Fahey; Methods Enzymol. 251, 148 (1995) | (11) M.T. Anderson, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 272, 107 (1999) | (12) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of biological dyes and stains (2010) | (13) S.I. Yakubu, et al.; J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2, 151 (2011) | (14) X. Shen, et al.; Methods Enzymol. 554, 31 (2015) | (15) B. Roda, et al.; Antioxidants 11, 939 (2022) | (16) N.Y. Mohsin, et al.; J. Fluoresc. (Epub ahead of print) (2024)





