Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
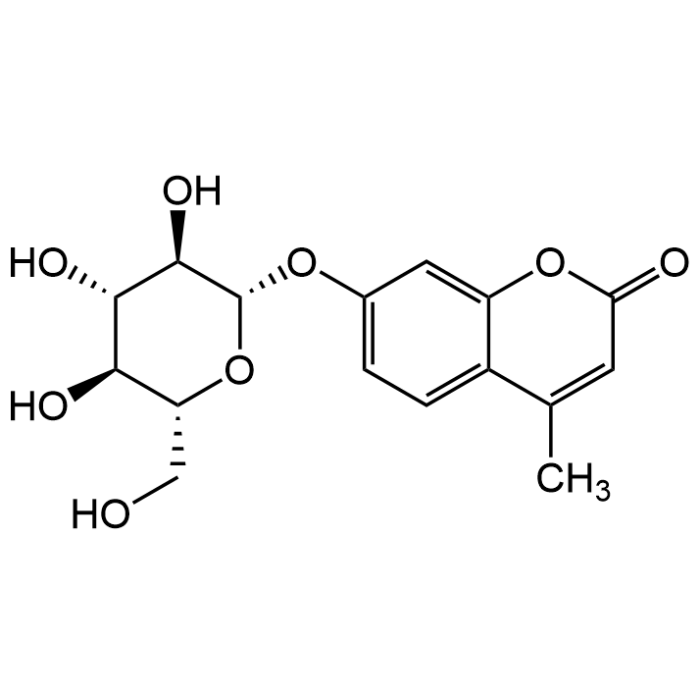
4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-D-glucopyranoside
As low as
110
CHF
CHF 110.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-M0099-G0011 gCHF 110.00
CDX-M0099-G0055 gCHF 451.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MUD; 4-MU-β-D-Glc; 4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-D-glucoside |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C16H18O8 |
| MW | 338.31 |
| CAS | 18997-57-4 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥97% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or DMF. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | YUDPTGPSBJVHCN-YMILTQATSA-N |
| Smiles | O[C@H]1[C@H](OC2=CC=C(C(C)=CC(O3)=O)C3=C2)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (MUD) is a non-fluorescent but sensitive fluorogenic substrate for β-glucosidase and β-glucocerebrosidase (also known as glucosylceramidase) yielding a blue fluorescent solution. It is a fluorogenic MU substrate for detecting glucosidase in cell extracts and purified enzyme preparations using a fluorescence microplate reader or fluorometer. It is employed in the detection of β-glucosidase as an indicator of Enterococci. It has been extensively used in work on Gaucher's disease, a lipid storage disease characterized by the accumulation of glucocerebroside due to a genetic deficiency of a β-glucosidase. The use of 4-Methylumbelliferyl-β-D-glucopyranoside has also been reported in a rapid method for identifying bacterial enzymes. Hydrolysis of MUD releases the fluorescent product 4-MU. Spectral Data. λEx/λEm= 360/450 nm (cleaved product, pH-dependent).
Product References
(1) S.P. Peters, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta 60, 391 (1975) | (2) D.M. Broadhead & J. Butterworth; Clin. Chim. Acta 75, 155 (1977) | (3) A. Basu & R.H. Glew; J. Biol. Chem. 260, 13067 (1985) | (4) K.J. Panosian & S.C. Edberg; J. Clin. Microbiol. 27, 1719 (1989) | (5) S. Nakagawa, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta. 118, 99 (1992) | (6) B. Setlow, et al.; J. Appl. Microbiol. 96, 1245 (2004) | (7) R. Kwapiszewski, et al.; Biomed. Microdevices 13, 431 (2011) | (8) M. Shanmuganathan & P. Britz-McKibbin; Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 399, 2843 (2011) | (9) L. Oftedal, et al.; Sci. Rep. 10, 22098 (2020)





