Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
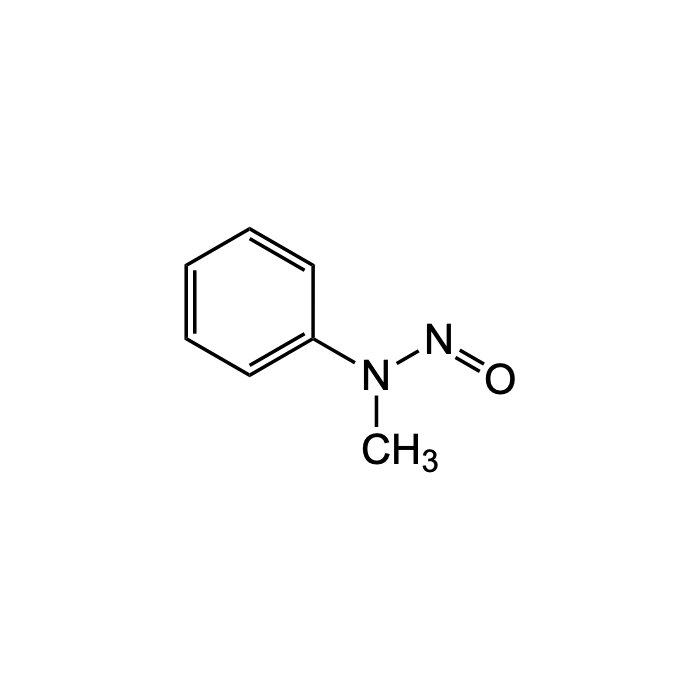
N-Nitrosomethylphenylamine (NMPA)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | NMPA; N-Methyl-N-nitrosoaniline; N-Methyl-N-nitrosobenzenamine; N-Methyl-N-phenylnitrosamine; NSC137 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C7H8N2O |
| MW | 136.15 |
| CAS | 614-00-6 |
| RTECS | BY5775000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (NMR) |
| Appearance | Orange liquid. |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in DMSO, methanol, ethanol or chloroform. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | MAXCWSIJKVASQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=NN(C)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
N-nitrosomethylphenylamine (NMPA) is a nitrosamine and is known to be a potent carcinogen associated with cancer development in animals and humans. NMPA can damage DNA and cause mutations in genes that control cell growth and division. It reacts with DNA in vitro to form genotoxic activity, which may lead to cell death or mutagenesis. NMPA is formed in various industrial processes, including the synthesis of certain chemicals. It serves as a building block in the synthesis of diverse compounds and functions as an analytical reagent for environmental monitoring. This compound can be used as analytical reference material. NMPA is useful for studying enzymatic denitrosation processes. NMPA could be used as a tumor initiator, as a reagent for preparing carcinogenic animal diseases model.
(1) C.M. Goodall, et al.; Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 17, 426 (1970) | (2) W. Lijinsky & R.M. Kovatch; Cancer Res. 48, 6648 (1988) | (3) S.R. Koepke, et al.; IARC Sci. Publ. 105, 346 (1991) | (4) T. Scheper, et al.; Chem. Biol. Interact. 77, 81 (1991) | (5) M. Stiborova, et al.; Cancer Lett. 110, 11 (1996) | (6) M. Stiborova, et al.; Cancer Lett. 138, 61 (1999) | (7) Y. Li & S.S. Hecht; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 4559 (2022) | (8) M. Bignami, et al.; Efsa J. 21, e07884 (2023)





