Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
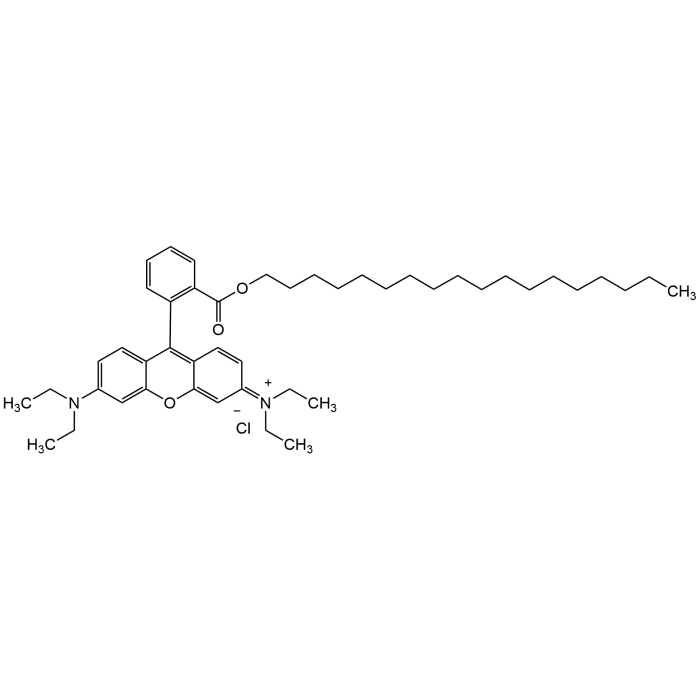
Octadecyl Rhodamine B chloride
As low as
329
CHF
CHF 329.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-O0014-M01010 mgCHF 329.00
CDX-O0014-M02525 mgCHF 657.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | R18 Cl; ORBC |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C46H67ClN2O3 |
| MW | 731.5 |
| CAS | 65603-19-2 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (TLC) |
| Appearance | Red solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (10mg/ml) or DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | NFGODEMQGQNUKK-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Smiles | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C2=C3C=CC(=[N+](CC)CC)C=C3OC4=C2C=CC(=C4)N(CC)CC.[Cl-] |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Octadecyl Rhodamine B chloride (R18) is a lipophilic fluorescent dye widely used in membrane biology and cell labeling studies. R18 is used in dequenching assays to monitor liposome fusion or virus-cell membrane fusion. It incorporates into plasma membranes for cell tracking, membrane dynamics, or cell-cell interaction studies. It can be used to label synthetic vesicles to study endocytosis, drug delivery, or membrane trafficking. R18 has also been used as acceptor in FRET studies on liposomes. The fluorescence of octadecyl rhodamine B in membranes is quenched at high dye concentration but is released at dilution. This property makes the dye useful for membrane fusion assays. Spectral Data: λEx/λEm (MeOH) = 556/580nm.
Product References
(1) D. Hoekstra, et al.; Biochem. 23, 5675 (1984) | (2) A. Stutzin, et al.; FEBS Lett. 197, 274 (1986) | (3) D. Hoekstra & K. Klappe K; Biosci. Rep. 6, 953 (1986) | (4) S. Tomlinson, et al.; Biochem. 28, 8303 (1989) | (5) L. Corazzi, et al.; J. Membr. Biol. 112, 123 (1989) | (6) J. Arnhold, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1191, 375 (1994) | (7) T. Reda, et al.; Mol. Membr. Biol. 12, 271 (1995) | (8) H. Hyogo, et al.; Dig. Dis. Sci. 44, 1662 (1999) | (9) A.A. Vallejo & M.S. Fernandez; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 480, 1 (2008) | (10) I. Trikash, et al.; Chem. Phys. Lipids 163, 778 (2010) | (11) T. Tian, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 228, 1487 (2013) | (12) Y.M.D. Gnopo & D. Putnam; Methods 177, 74 (2020)





