Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
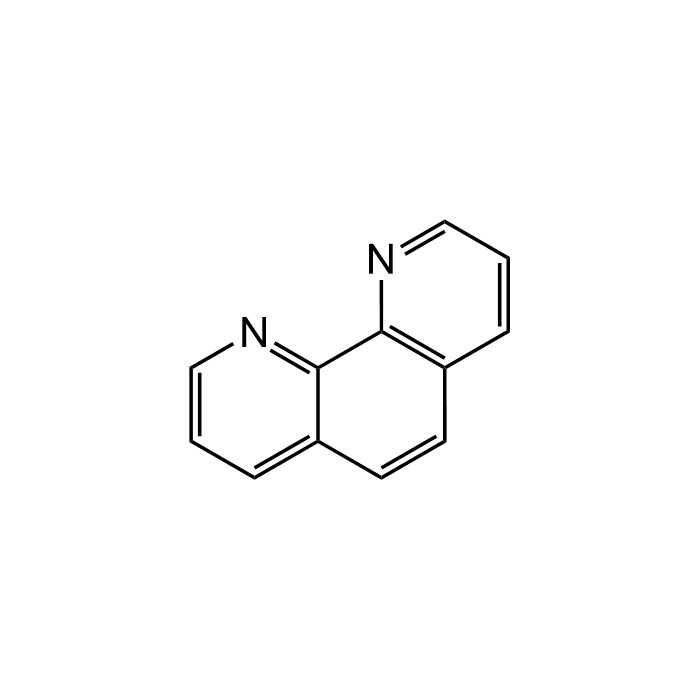
1,10-Phenanthroline
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | o-Phenanthroline; 4,5-Diazaphenanthrene; β-Phenanthroline; TS20; NSC203545 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C12H8N2 |
| MW | 180.21 |
| CAS | 66-71-7 |
| RTECS | SF8300000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or ethanol (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | DGEZNRSVGBDHLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | C12=CC=CN=C1C3=C(C=CC=N3)C=C2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
1,10-Phenanthroline is a heterocyclic organic compound, which forms complexes with metal ions. It is a versatile ligand employed in the spectrophotometric determination of metals and photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. The complexes that are build have wide applications in biochemistry, catalysis and analytical chemistry. 1,10-Phenanthroline is a ligand used in a mild, copper (II)-catalyzed cross-coupling of organoboronic acids and sulfinate salts leading to aryl- and alkenylsulfones. It is a conventional chelator to study its efficacy in Fenton's reaction-luminol chemiluminescence system. 1,10-Phenanthroline enhances hPSC differentiation into cranial placode cells and is known as a non-specific matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor. 1,10-Phenanthroline is also used as a building block for metallomacrocycles and other biological active compounds, such as anti-cancer agents.
(1) G. Hoyer, et al.; Scand. J. Clin. Lab Invest. 2, 125 (1950) | (2) M.M. Jones & D.O. Johnston; Nature 216, 509 (1967) | (3) K. Kobashi; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 158, 239 (1968) | (4) H.M. Butler, et al.; Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 47, 541 (1969) | (5) M. Kito & R. Urade; Met. Ions Biol. Syst. 38, 187 (2001) (Review) | (6) M. McCann, et al.; Curr. Med. Chem. 19, 2703 (2012) (Review) | (7) J. Tchieu, et al.; Cell Stem Cell 21, 399 (2017) | (8) N. Georgi, et al.; J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 11, 724 (2017) | (9) S. Masuri, et al.; Molecules 27, 49 (2021) (Review) | (10) W.A. Souza, et al.; J. Inorg. Biochem. 237, 111993 (2022) | (11) U. Bildziukevich, et al.; Org. Biomol. Chem. 20, 8157 (2022) | (12) M.M. Cetin, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 13, 980479 (2022) | (13) N.A. Ashashi, et al.; ACS Omega 7, 41370 (2022) | (14) D. Zhang, et al.; Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 295, 122608 (2023)





