Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
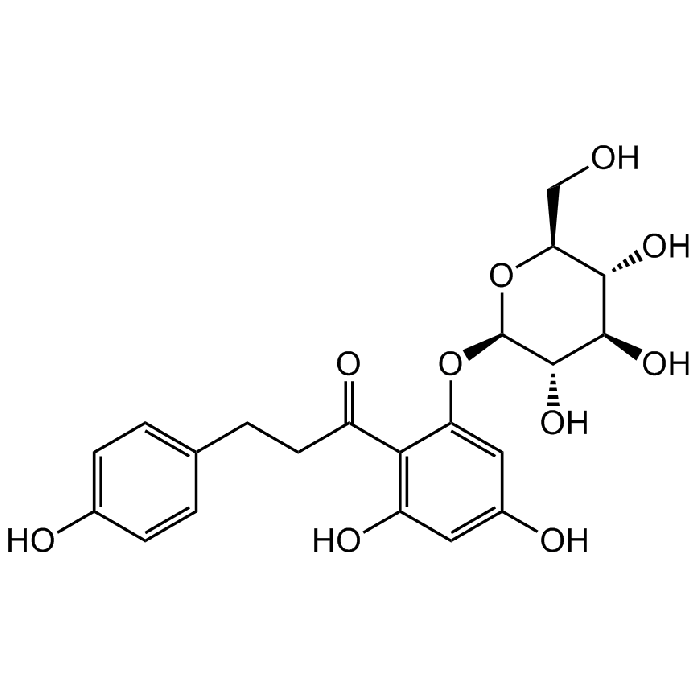
Phloridzin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Floridzin; Phloretin 2'-glucoside; Phloridzosid; Phlorizin; NSC 2833 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C21H24O10 |
| MW | 436.413 |
| CAS | 60-81-1 |
| RTECS | UC2080000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Light yellow to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml), DMF (20mg/ml) or ethanol (5mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | IOUVKUPGCMBWBT-RQUKQETFSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=CC=C(CCC(C2=C(O)C=C(O)C=C2O[C@@H]3[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](CO)O3)=O)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Phlorizin is a natural product, first isolated from the bark of apple trees, that reduces plasma glucose levels by blocking renal and intestinal glucose absorption through inhibition of SGLT1 and SGLT2. It competitively inhibits (competes with D-glucose) the initial rate of α-methyl-D-glucopyranoside (α-MDG) uptake in the nM range. Phlorizin has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and to have antioxidant properties. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) is a high affinity, low capacity transporter abundant in the small intestine, with some expression in the kidney as well. SGLT2 is a low affinity, high capacity transporter in the kidney that accounts for approximately 90% of glucose reabsorption into the blood stream. Selective inhibition of SGLT2 is a potential strategy for reducing plasma glucose levels as a treatment for diabetes.
(1) G. Toggenburger, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 688, 557 (1982) | (2) N. Oulianova, et al.; J. Membr. Biol. 179, 223 (2001) | (3) K.P. Briski & E.S. Marshall; Neurochem. Res. 26, 783 (2001) | (4) R.J. McCrimmon, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 283, E1076 (2002) | (5) J.R.L. Ehrenkranz, et al.; 21, 31 (2005) (Review) | (6) J.R. White; Clin. Diabet. 28, 5 (2010) | (7) C.S. Hummel, et al.; Am. J. Phys. cell Phys. 300, C14 (2011) | (8) C.S. Hummel, et al.; Am. J. Phys. cell Phys. 302, C373 (2012) | (9) T. Nagata, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 306, F1520 (2014) | (10) Y. Katsuda, et al.; Exp. Anim. 64, 161 (2015) | (11) M. Raja & R.K. Kinne; Biochimie 115, 187 (2015) | (12) X. Mei, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 7502 (2016) | (13) R.A. Mendes, et al.; J. Mol. Model 24, 101 (2018)





