Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
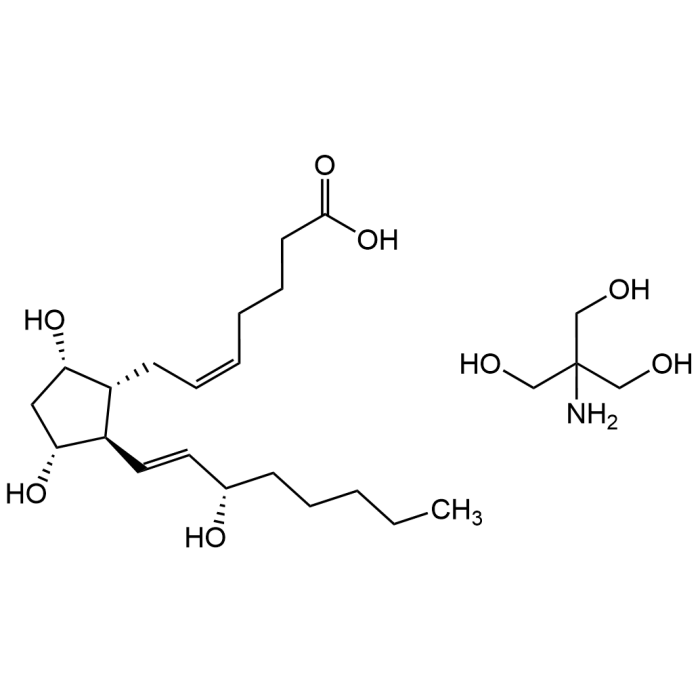
Prostaglandin F2α tromethamine salt
As low as
116
CHF
CHF 116.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-P0320-M0055 mgCHF 116.00
CDX-P0320-M01010 mgCHF 142.00
CDX-P0320-M02525 mgCHF 284.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Dinoprost trometamol; PGF2α tromethamine; Prostaglandin F2α THAM salt; Prostaglandin F2α tris salt; Lutalyse; U 14583E; NSC 196515; Minprostin F2α; Enzaprost T |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C20H34O5 . C4H11NO3 |
| MW | 475.62 |
| CAS | 38562-01-5 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (TLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or methanol (all 50 mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | IYGXEHDCSOYNKY-RZHHZEQLSA-N |
| Smiles | OC(CCC/C=C\C[C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H](C[C@@H]1O)O)/C=C/[C@@H](O)CCCCC)=O.OCC(CO)(N)CO |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | -20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) is a widely distributed prostaglandin occurring in many species. It causes contraction of vascular, bronchial, intestinal, and myometrial smooth muscle, and also exhibits potent luteolytic activity. Mechanistically, it acts via activation of the FP (prostaglandin F2α) receptor to raise intracellular calcium, driving smooth muscle contraction and facilitating luteolysis. This makes it a versatile agent both for controlled reproductive interventions and as a key tool in physiological and pharmacological research. PGF2α exhibits its receptor mediated physiological activity at 50-100nM.
Product References
(1) L. Speroff & P.W. Ramwell; Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 107, 1111 (1970) | (2) B. Samuelsson, et al.; Annu. Rev. Biochem. 47, 997 (1978) | (3) K. Watanabe, et al.; PNAS 83, 1583 (1986) | (4) D.J. Crankshaw & V. Gaspar; J. Reprod. Fertil. 103, 55 (1995) | (5) C.W. Miller, et al.; Endocrinol. 137, 5641 (1996) | (6) F.J. Diaz, et al.; Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 191, 65 (2002) | (7) S. Basu; Med. Res. Rev. 27, 435 (2007) | (8) D. Agas, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 228, 25 (2013) | (9) J. Kim & M. Shim; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853, 500 (2015) | (10) E. Goupil, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 290, 3137 (2015)





