Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
Propiconazole solution (100μg/ml in acetonitrile)
As low as
155
CHF
CHF 155.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-P0414-L0055 mlCHF 155.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | PPZ; CGA 64250; CGD 92710F; Proconazole; Microban S 2140 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
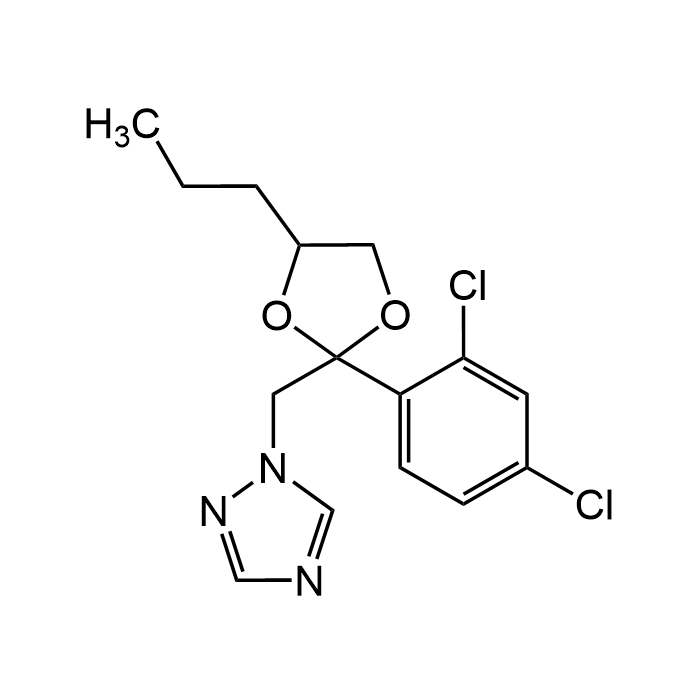
| Formula | C15H17Cl2N3O2 |
| MW | 342.22 |
| CAS | 60207-90-1 |
| RTECS | XZ4620000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (NMR) |
| Appearance | Liquid. 100 μg/ml in acetonitrile. |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetonitrile and buffer. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | STJLVHWMYQXCPB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | ClC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1C2(CN3N=CN=C3)OC(CCC)CO2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Propiconazole is a broad-spectrum triazole fungicide that inhibits ergosterol biosynthesis via the demethylation of C-14, leading to fungal cell membrane disruption. Formulations containing propiconazole have been used in the control of fungi in agriculture. It inhibits S. cerevisiae, but not rat liver, microsomal cytochrome P450. Propiconazole inhibits the growth of T. deformans and R. stolonifer, as well as A. niger, M. fructigena, S. nodorum, T. harzanium, R. solani, and S. rolfsii at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 5 ppm. This compound can be used as analytical reference material. Propiconazole increases production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), the number of DNA mutations, and the incidence of tumor formation in mouse liver. Shown to activate PXR and disrupt hepatic metabolism in mice.
Product References
(1) H. Vanden Bossche, te al.; Pestic. Sci. 15, 188 (1984) | (2) M. Sancholle, et al.; Pest. Biochem. Phys. 21, 31 (1984) | (3) J.A. Zarn, et al.; Environ. Health Perspect. 111, 255 (2003) | (4) M. Calonne, et al.; Chemosphere 87, 376 (2012) | (5) C.S. Mazur, et al., Toxicol. Lett. 232, 37 (2015) | (6) N.O. Costa, et al.; Toxicology 335, 55 (2015) | (7) J. Valades, et al.; Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 26, 27808 (2019) | (8) B. Attema, et al; Arch. Toxicol. (Epub ahead of print) (2024)





