Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
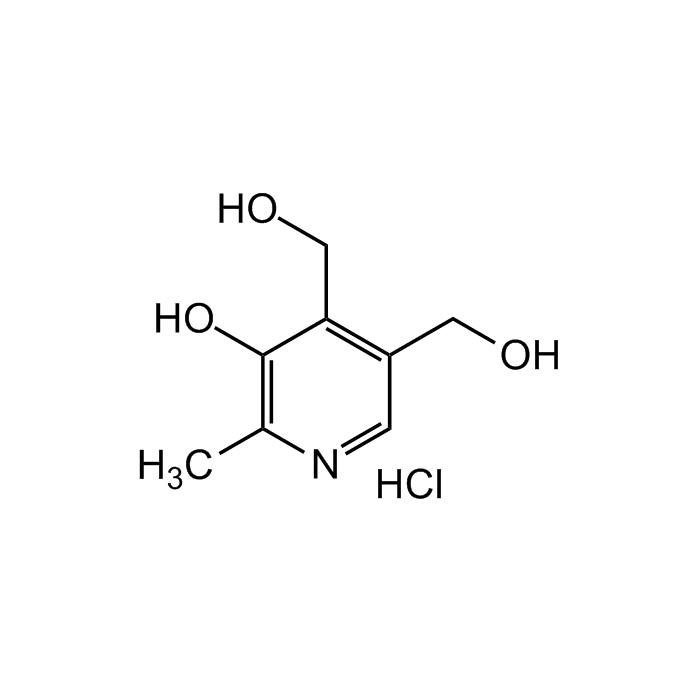
Pyridoxine hydrochloride
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Adermine hydrochloride; Vitamin B6 hydrochloride; Pyridoxol hydrochloride |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C8H11NO3 . HCl |
| MW | 205.64 |
| CAS | 58-56-0 |
| RTECS | UV1350000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (50mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ZUFQODAHGAHPFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OCC1=C(CO)C=NC(C)=C1O.Cl |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Pyridoxine hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of pyridoxine (vitamin B6), a water-soluble vitamin B. Pyridoxine hydrochloride is converted into the active form, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP), an essential cofactor in many enzymatic activities including synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters and sphingolipids. This vitamin is essential to red blood cell, nervous system, and immune systems functions and helps maintain normal blood glucose levels. It is required for muscle phosphorylase activity associated with glycogen metabolism. Vitamin B6 is essential to maintain the health of nerves, skin and red blood cells. It is also used to treat nerve disorder (peripheral neuropathy) and hereditary disorders like xanthurenic aciduria, cystathioninuria, hyperoxaluria and homocystinuria. It finds application in cosmetics, food and feed additives.
(1) E.E. Snell; Physiol. Rev. 33, 509 (1953) | (2) M. Ebadi; Neurochem. Int. 3, 181 (1981) | (3) S. Dakshinamurti & K. Dakshinamurti; Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 93, 1083 (2015) (Review) | (4) D. Bueno Dalto & J.-J. Matte; Nutrients 9, 189 (2017) (Review) | (5) N.E.R. Abosamak & V. Gupta; StatPearls (2020)





