Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
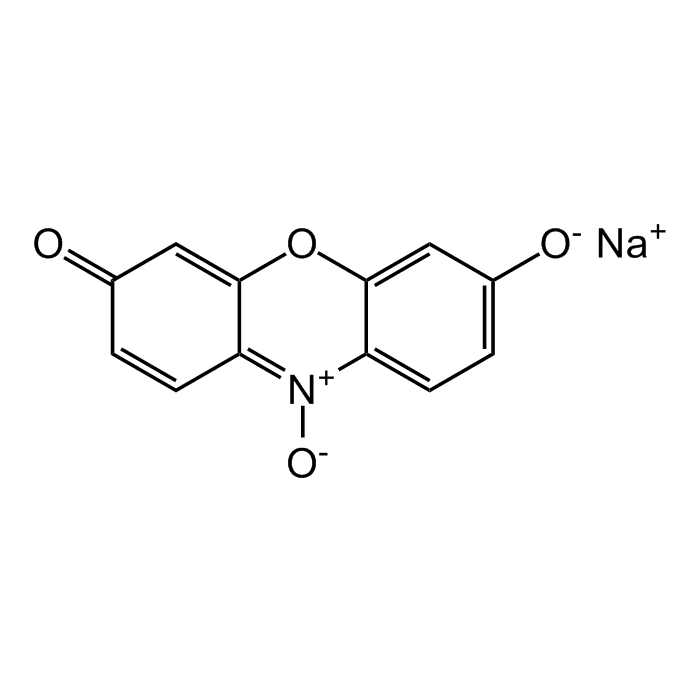
Resazurin sodium salt
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Alamar Blue; Vybrant; UptiBlue; 7-Hydroxy-3H-phenoxazin-3-one-10-oxide sodium salt |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C12H6NNaO4 |
| MW | 251.17 |
| CAS | 62758-13-8 |
| RTECS | SP7700000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ~80% (Dye Content) (UV/Vis). Suitable for cell culture application. |
| Appearance | Black-Violet solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | IVGPGQSSDLDOLH-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Smiles | [Na+].[O-]C1=CC=C2C(OC3=CC(=O)C=CC3=[N+]2[O-])=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Resazurin (also known as Alamar Blue), is the N-oxide of the fluorescent dye resorufin. It is useful for detecting reductive activities in cells and has been widely used for measuring cell proliferation and mitochondrial metabolic activity. It is used as a quantifiable detection agent for enzyme activity assays and as an oxidation-reduction indicator in cell proliferation, cell viability and cytotoxicity assays.
Resazurin is a non-toxic, water-soluble and redox-sensitive dye that is non-fluorescent until it is reduced to the highly red fluorescent resorufin (λEx/λEm: 563/587 nm). Usually, NADPH or NADH is the reductant that converts resazurin to resorufin in the presence of diaphorase as the enzyme. Thus, resazurin can be used to detect NADH, NADPH, or diaphorase levels. Furthermore, the resazurin/diaphorase/NADPH system can be used to detect any biochemical or enzyme activity that is involved in a biochemical reaction generating NADH or NADPH.
(1) J. O'Brien, et al.; Eur. J. Bioch. 267, 5421 (2000) | (2) D.P. Penney, et al.; Biotech. Histochem. 77, 237 (2002) | (3) S.N. Rampersad; Sensors 12, 12347 (2012) | (4) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of Fluorescent Dyes and Probes 370 (2015) | (5) M. Koyanagi, et al.; Cytotechnology 68, 1489 (2016)






