Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
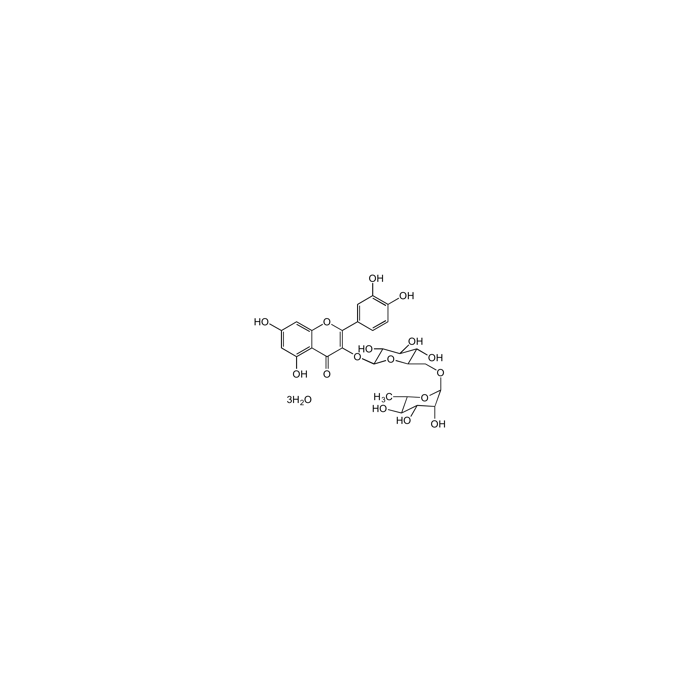
Rutin trihydrate
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Rutoside; Phytomelin; Sophorin; Birutan; Eldrin; Birutan Forte; Rutin trihydrate; Globularicitrin; Violaquercitrin; Quercetin rutinoside |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C27H30O16 . 3H2O |
| MW | 664.5 |
| CAS | 250249-75-3 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Light yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or pyridine. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | IKGXIBQEEMLURG-KAOWGYSOSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1C2=C(O)C=C(O)C=C2OC(C3=CC(O)=C(O)C=C3)=C1O[C@H]4[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO[C@H]5[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(C)O5)O4 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
A polyphenolic flavonoid that acts as an antioxidant and NO scavenger. It can attenuate peroxide production in glial cells by acting as a free radical scavenger and protect renal cells from oxidative injury. Inclusion of rutin in the diet of rats significantly reduced the appearance of single-strand breaks in nuclear DNA caused by hepatocarcinogens aflatoxin B1 and N-nitrosodiumethylamine. This protection from DNA damage was found to be due to a reduction in the induction of repair enzymes polymerase, DNA polymerase β and DNA ligase. Since DNA damage and inefficient repair are thought to initiate the process of carcinogenesis, effects of rutin on these functions suggests a protective role of this flavonoid against carcinogenesis induced by chemical carcinogens. Rutin ameliorates obesity through brown fat activation.
(1) I.B. Afanas'ev, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 38, 1763 (1989) | (2) R.P. Webster, et al.; Cancer Lett. 109, 185 (1996) | (3) E.A. Ostrakhovitch & I.B. Afanas'ev; Biochem. Pharmacol. 62, 743 (2001) | (4) N. Kamalakkannan & P.S. Prince; Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 98, 97 (2006) | (5) J.P. Lin, et al.; Leuk. Res. 33, 823 (2009) | (6) R. Lapa Fda, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 63, 875 (2011) | (7) S.W. Wang, et al.; Neurotoxicology 33, 482 (2012) | (8) X. Yuan, et al.; FASEB J. 31, 333 (2016)






