Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
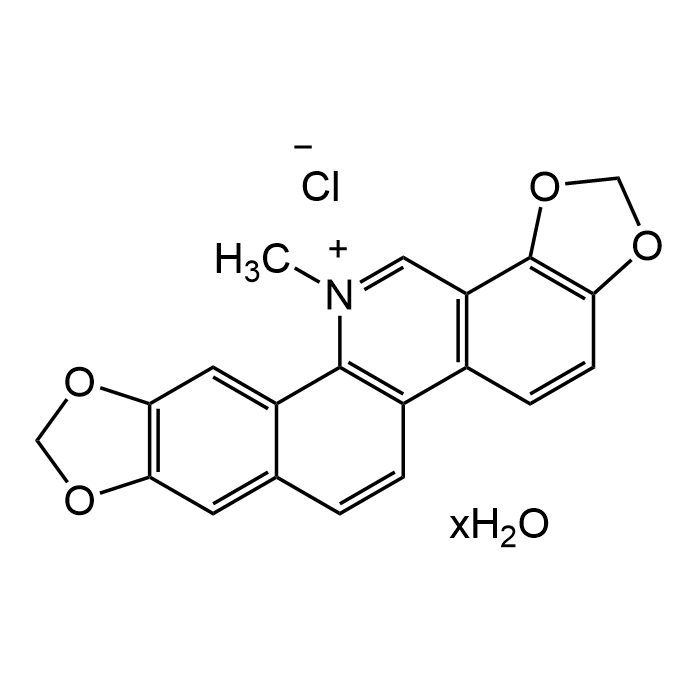
Sanguinarine chloride hydrate
As low as
168
CHF
CHF 168.00
In stock
Only %1 left
CDX-S0377-M01010 mgCHF 168.00
CDX-S0377-M05050 mgCHF 509.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Sanguinarine hydrochloride |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C20H14ClNO4 . xH2O |
| MW | 367.78 (anhydrous basis) |
| CAS | 5578-73-4 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Semisynthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Faint orange to dark orange powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (3mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | XJCOXSCAMNPLFI-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Smiles | C[N+]1=CC2=C(C=CC3=C2OCO3)C4=C1C5=CC(OCO6)=C6C=C5C=C4.[Cl-] |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Sanguinarine chloride is a quaternary ammonium benzophenanthine alkaloid found in traditional herbs such as Chelidonium, Corydalis, Sanguinarum, and Borovula. It has been proven to possess broad-spectrum biological activities, such as antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antiosteoporosis, neuroprotective, immune regulatory, cardiovascular, antibacterial, antiviral and antiparasitic activities. Sanguinarine chloride is an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C), selective over PP1, PP2A and PP2B in vitro. It inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1), JNK, MAPK, NF-kB, STAT3, MMP-2, MMP-9 and other kinases. Sanguinarine chloride blocks cell cycle in the G1 phase, stimulates apoptosis via induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), disrupts the microtubule assembly and causes DNA damage resulting the death of the cancer cells.
Product References
(1) K.C. Godowski; J. Clin. Dent. 1, 96 (1989) (Review) | (2) M.M. Chaturvedi, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30129 (1997) | (3) A. Vogt, et al; J. Biol. Chem. 280, 19078 (2005) | (4) N. Aburai, et al; Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 74, 548 (2010) | (5) M.H. Han, et al.; Toxicol. Lett. 220, 157 (2013) | (6) S. Pallichankandy, et al.; Free Redic. Biol. Med. 89, 708 (2015) | (7) P. Basu & G.S. Kumar; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 928, 155 (2016) (Review) | (8) I.W. Achkar, et al.; Future Med. Chem. 9, 933 (2017) (Review) | (9) S. Galadari, et al.; Phytomed. 34, 143 (2017) (Review) | (10) L.J. Huang, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 173, 116406 (2024) (Review)





