Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
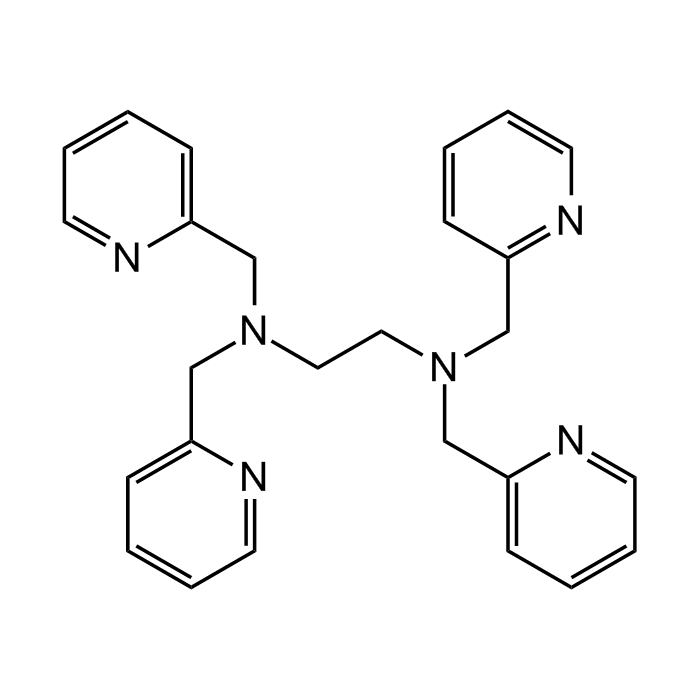
N,N,N',N'-Tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | TPEN; TPEDA |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C26H28N6 |
| MW | 424.5 |
| CAS | 16858-02-9 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform or ethanol (10mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | CVRXLMUYFMERMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | N(CC1=CC=CC=N1)(CC2=CC=CC=N2)CCN(CC3=NC=CC=C3)CC4=CC=CC=N4 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
TPEN is a cell permeable metal ion chelator. TPEN is a chelator that has a high affinity for zinc (Zn2+), next to other transition metals (Zn2+ >Fe2+ >Mn2+) and is used in zinc treatment studies to limit intra- and extracellular concentrations of the mineral. TPEN has lower affinity for Ca2+ and Mg2+ and can also form complexes with other soft metal ions such as Cd2+. In addition to a heavy metal chelator, TPEN is also known to be an apoptosis inducer. Depletion of zinc by TPEN induces apoptosis in several cell lines. TPEN shows anticancer activity through induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis, via reactive oxygen species (ROS) signaling mechanism and inhibiting cell autophagy. TPEN also inhibits RNA binding protein Lin28 and has been shown to be useful in extracting Aβ depostis from Alzheimer's disease brain tissue.
(1) F. Chimienti, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 6, 51 (2001) | (2) J. Fonte, et al.; J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 3, 209 (2001) | (3) Y.E. Cho, et al.; Nutr. Res. Pract. 1, 29 (2007) | (4) U. Rana, et al.; J. Inorg. Biochem. 102, 489 (2008) | (5) P. Makhov, et al.; Cell Death Diff. 15, 1745 (2008) | (6) P.J. Bernal, et al.; Circul. Res. 102, 1575 (2008) | (7) C.M. Matias, et al.; J. Fluoresc. 20, 377 (2010) | (8) A.J. Morgan, et al.; Cell Calcium. 52, 481 (2012) | (9) O.N. Rahal, et al.; Cancer Biol. Ther. 17, 1139 (2016) | (10) F. Zhang, et al.; Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 37, 235 (2017) | (11) L. Wang, et al.; Cell Rep. 23, 3091 (2018) | (12) V. Soto-Mercado, et al.; Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 18, 1617 (2018) | (13) Z. Yu, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 234, 20648 (2019) | (14) M. Mendivil-Perez, et al.; Biometals 34, 49 (2021)





