Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
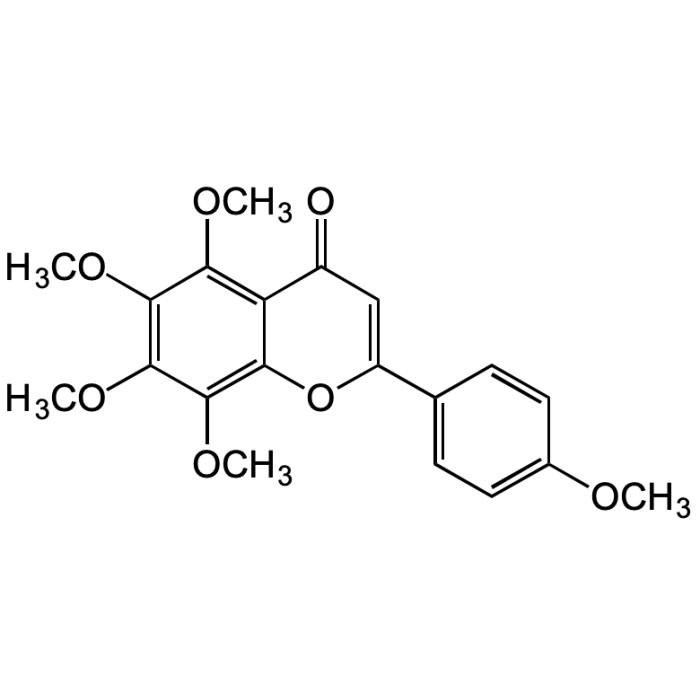
Tangeretin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 4',5,6,7,8-Pentamethoxyflavone; NSC 53909; NSC 618905; Ponkanetin; 5,6,7,8-Tetramethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C20H20O7 |
| MW | 372.37 |
| CAS | 481-53-8 |
| RTECS | DJ3102725 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from plant source. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to pale yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or DMF (10mg/ml). Sparingly soluble in ethanol (0,5 mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ULSUXBXHSYSGDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1C=C(C2=CC=C(OC)C=C2)OC3=C(OC)C(OC)=C(OC)C(OC)=C31 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Tangeritin is a polymethoxylated flavone isolated from peels of citrus fruits with antiproliferative and antioxidant properties. It inhibits signaling in cancer cells, reducing ERK phosphorylation and growth of estradiol-stimulated T47D breast cancer cells and blocking p38 MAPK, JNK, and Akt activation in interleukin-1β-stimulated human lung carcinoma A549 cells. It is described to block cell cycle progression at G1 and induce apoptosis. Shows anti-inflammatory, osteoprotective and neuroprotective effects. Tangeritin activates the pregnane X receptor, inducing MDR1 expression in human colonic LS180 cancer cells. Shown to be a Notch-1 inhibitor. Tangeretin stimulates glucose uptake via regulation of AMPK signaling pathways and has been shown to antagonize ABCB1-mediated multidrug resistance.
(1) T. Hirano, et al.; Br. J. Cancer 72, 1380 (1995) | (2) C. Chaumontet, et al.; Cancer Lett. 114, 207 (1997) | (3) S. Kawaii, et al.; Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63, 896 (1999) | (4) K.P. Datla, et al.; Neuroreport 12, 3871 (2001) | (5) M.H. Pan, et al.; Carcinogenesis 23, 1677 (2002) | (6) S. Van Slambrouck, et al.; FEBS Lett. 579, 1665 (2005) | (7) K.H. Chen, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 73, 215 (2007) | (8) K.L. Morley, et al.; Cancer Lett. 251, 168 (2007) | (9) H. Satsu, et al.; J. Agricult. Food Chem. 56, 5366 (2008) | (10) M.S. Kim, et al.; Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 358, 127 (2012) | (11) Z. Shu, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 19, 275 (2014) | (12) Y.Y. Lee, et al.; J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 11, 294 (2016) | (13) S.L. Feng, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 110, 193 (2016) | (14) L.L. Ma, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 81, 491 (2016) | (15) N. Braidy, et al.; CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 16, 387 (2017) (Review) | (16) S. Xu, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 72, 402 (2019)





