Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
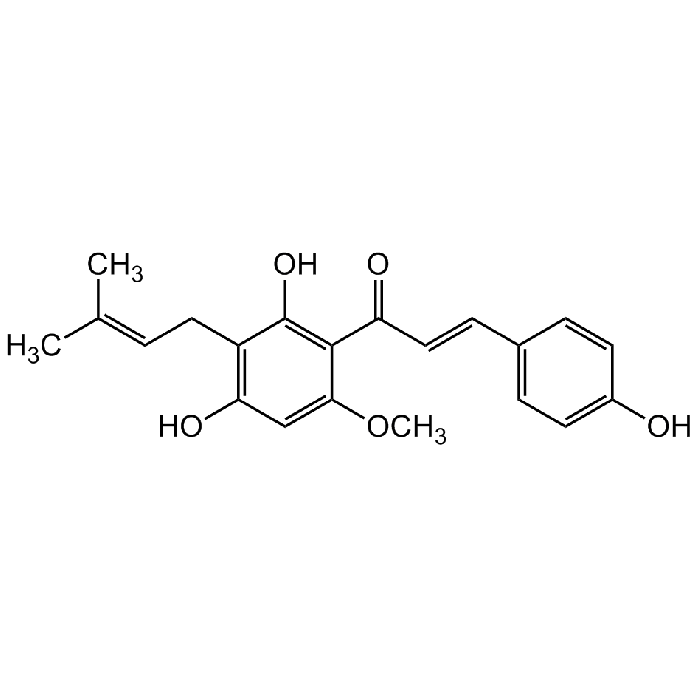
Xanthohumol
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 2',4,4'-Trihydroxy-6'-methoxy-3'-prenylchalcone |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C21H22O5 |
| MW | 354.4 |
| CAS | 6754-58-1 |
| RTECS | UD5574117 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (NMR) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or ethanol (10mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ORXQGKIUCDPEAJ-YRNVUSSQSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=C(C(/C=C/C2=CC=C(O)C=C2)=O)C(OC)=CC(O)=C1C/C=C(C)/C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Xanthohumol is a cell-permeable natural prenylated chalcone isolated from the hop plant, H. lupulus. Xanthohumol and its metabolites induce protective detoxification enzymes, at least in part via the nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 pathway. Xanthohumol can have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, antidiabetic and osteogenic effects. Xanthohumol binds to the N-terminal domain of p97 ATPase (VCP; valosin-containing protein), an essential protein for autophagosome maturation. Xanthohumol inhibits the function of p97 ATPase thereby impairing autophagosome maturation and resulting in accumulation of the microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3-II (LC3-II)1. Xanthohumol inhibits diacylglycerol acetyltransferase (DGAT) and human P450 enzymes. It also inhibits the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF under hypoxic conditions.
(1) N. Tabata, et al.; Phytochemistry 46, 683 (1997) | (2) J.F. Stevens & J.E. Page; Phytochemistry 65, 1317 (2004) (Review) | (3) C. Gerhauser; Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 49, 827 (2005) (Review) | (4) P.J. Magalhaes, et al.; Nat. Prod. Commun. 4, 591 (2009) (Review) | (5) J. Inokoshi, et al.; J. Antibiot. 62, 51 (2009) | (7) R. Vene, et al.; Mol. Med. 18, 1292 (2012) | (8) Y. Sasazawa, et al.; ACS Chem. Biol. 7, 892 (2012) | (9) V. Krajka-Kuzniak, et al.; Toxicol. In Vitro 27, 149 (2013) | (10) R. Costa, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 76, 2047 (2013) | (11) T. Schilling, et al.; J. Ster. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 139, 252 (2014) | (12) M. Liu, et al.; Molecules 20, 754 (2015) (Review) | (13) C.H. Jiang, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 9, 530 (2018) (Review)





