Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
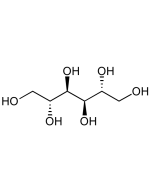
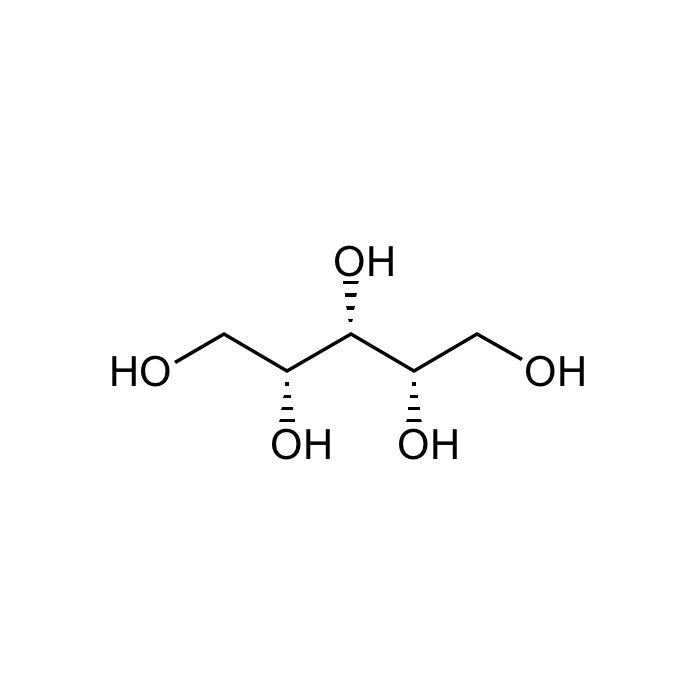
Xylitol
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Xylite; BRN 1720523; NSC 25283 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C5H12O5 |
| MW | 152.15 |
| CAS | 87-99-0 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White crystals or crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-SCDXWVJYSA-N |
| Smiles | O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](CO)O)O)CO |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Sugar alcohol used as a sweetener. Unlike other natural or synthetic sweeteners, xylitol is actively beneficial for dental health by reducing caries (cavities) to a third in regular use and helpful to remineralization. Fair evidence was found that xylitol (as chewing gum, lozenges, nasal spray, etc.) reduced the incidence of acute middle ear infection in healthy children. Cavity-causing bacteria prefer six-carbon sugars or disaccharides, while xylitol is non-fermentable and cannot be used as an energy source - while still being taken up into the cell (due to similar shape) and interfering with bacterial growth and reproduction. The harmful micro-organisms are starved in the presence of xylitol, allowing the mouth to remineralize damaged teeth with less interruption. Possessing approximately 33% fewer calories, xylitol is a lower-calorie alternative to table sugar. Proven beneficial in metabolic syndrome patients, including insulin resistance, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and an increased risk for blood clots.
(1) J.L. Danhauer, et al.; Int. J. Audiol. 49, 754 (2010) | (2) K.K. Maekinen; Med. Princ. Pract. 20, 303 (2011) | (3) M.E. Peterson; Top. Companion Anim. Med. 28, 18 (2013) | (4) P.A. Nayak, et al.; Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 6, 89 (2014) | (5) S. Ur-Rehman, et al.; Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 55, 1514 (2015) | (6) A.S. Ferreira, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 16, 35 (2015)