Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
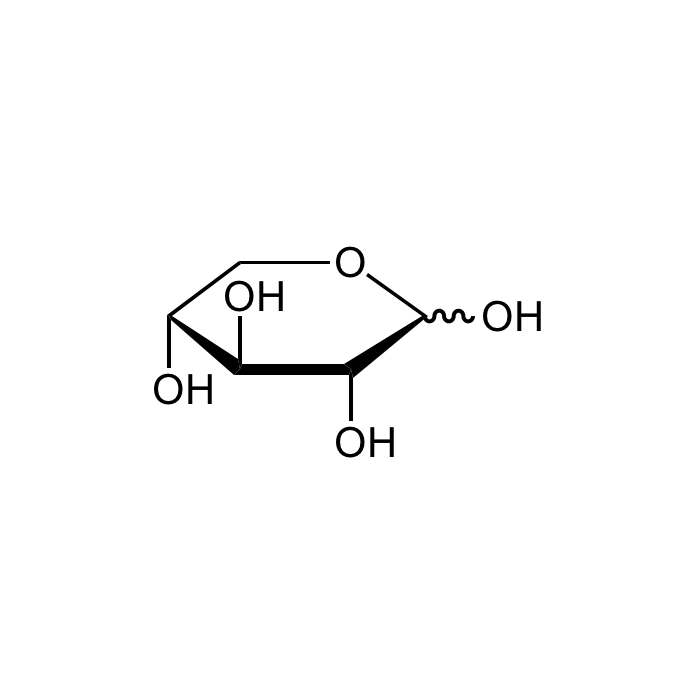
D-(+)-Xylose
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | D-Xylose; (+)-Xylose; Wood sugar |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C5H10O5 |
| MW | 150.13 |
| CAS | 58-86-6 |
| RTECS | ZF2285000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from plant source. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (50mg/ml). |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | SRBFZHDQGSBBOR-IOVATXLUSA-N |
| Smiles | O[C@H]1[C@H](O)COC(O)[C@@H]1O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
D-(+)-Xylose is classified as a monosaccharide of the aldopentose type, which means that it contains five carbon atoms and includes an aldehyde functional group. It is derived from hemicellulose, one of the main constituents of biomass. Like most sugars, it can adopt several structures depending on conditions. With its free aldehyde group, it is a reducing sugar. D-(+)-Xylose has been used as one of the component to stimulate microbial activity, for the enhancement of biofilm formation, as a part of biochemical tests for the identification of B. cereus group and for substrate screening characterization. Estimation of D-(+)-Xylose in the urine after oral administration, is useful in diagnosing absorption of carbohydrates and malabsorption of non-pancreatic molecules. D-(+)-Xylose plays a significant role in the biologically conversion of plant biomass to fuels and chemicals.
(1) G.E. Demetrakopoulos & H. Amos; World Rev. Nutr. Diet 32, 96 (1978) | (2) T.W. Jeffries; Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 27, 1 (1983) | (3) R.M. Craig & A.J. Atkinson; Gastroenterology 95, 223 (1988) | (4) B. Asboth & G. Naray-Szabo; Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 1, 237 (2000) | (5) M.B. Fusaro, et al.; Carbohydr. Res. 409, 9 (2015) | (6) K.N.G. Valdehuesa, et al.; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102, 7703 (2008) | (7) S.S. Jagtap & C.V. Rao; Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102, 9015 (2018) | (8) S. Kwak, et al.; Biotechnol. Adv. 37, 271 (2019) | (9) X. Li, et al.; Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 57, 56 (2019)





