Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
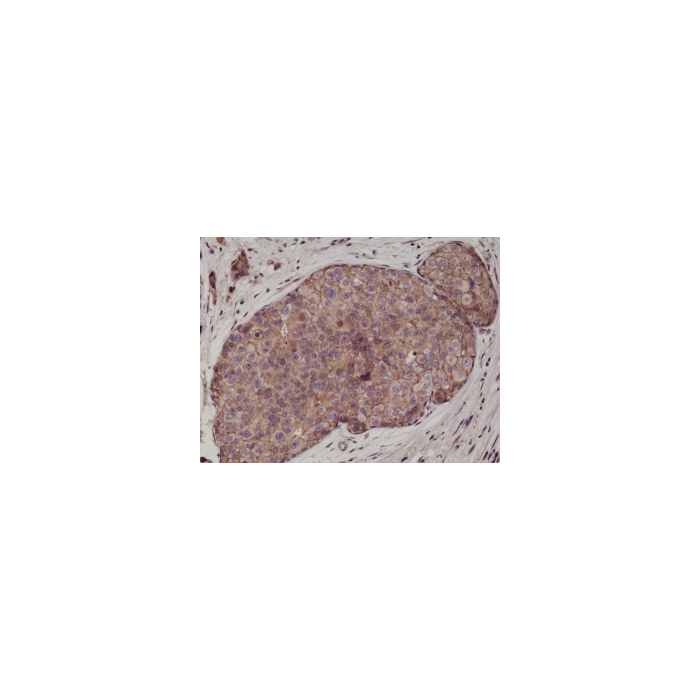
anti-E-Cadherin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM244)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CDH1; CAM 120/80; CD324 |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM244 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | A peptide corresponding to Cadherin-1. |
| Application |
Immunohistochemistry (IHC): 1:500-1:1000 dilution |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Specificity |
This antibody reacts to human E-cadherin (Cadherin-1). |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Concentration | N/A |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Accession Number | P12830 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Cadherins are a superfamily of transmembrane glycoproteins that contain cadherin repeats of approximately 100 residues in their extracellular domain. Cadherins mediate calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion and play critical roles in normal tissue development. The classic cadherin subfamily includes N-, P-, R-, B-, and E-cadherins, as well as about ten other members that are found in adherens junctions, a cellular structure near the apical surface of polarized epithelial cells. E-Cadherin (epithelial cadherin) is a calcium dependent cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein comprised of five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail. Mutations in this gene are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid and ovarian cancer. Loss of function is thought to contribute to progression in cancer by increasing proliferation, invasion, and/or metastasis. E-cadherin plays a central role in the growth and development of cells by controlling tissue architecture, and maintenance of tissue integrity. Studies have demonstrated that reduction and/or loss of E-cadherin expression in carcinomas correlates positively with the potential of these tumors for invasion and metastasis.





