Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
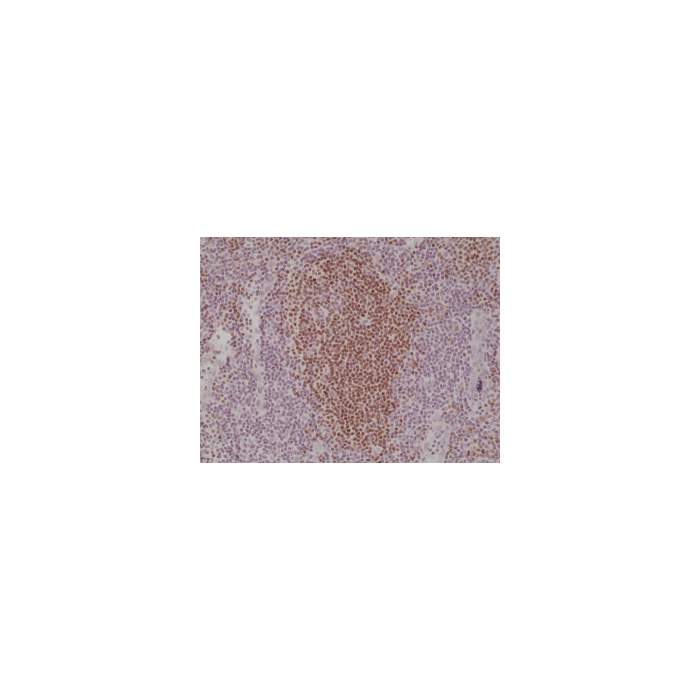
anti-PAX-5 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM331)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Paired Box Protein Pax-5; B-cell-specific Transcription Factor; BSAP |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM331 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | A peptide corresponding to C-terminus of human Paired box protein Pax-5. |
| Application |
Immunohistochemistry (IHC): 1:500-1:1000 dilution |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Specificity |
This antibody reacts to human Paired box protein Pax-5. It may also react to mouse Paired box protein Pax-5, as predicted by immunogen homology. |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Concentration | N/A |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Accession Number | Q02548 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
PAX-5 is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of transcription factors. The PAX proteins are important regulators in early development and alterations in the expression of their genes are thought to contribute to neoplastic transformation. PAX-5 is the B-cell lineage specific activator protein (BSAP) that is expressed at early, but not late stages, of B-cell differentiation. Its expression has also been detected in developing CNS and testis, therefore, PAX-5 may not only play an important role in B-cell differentiation, but also in neural development and spermatogenesis. Mutations in the gene can result in leukemia.





