Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
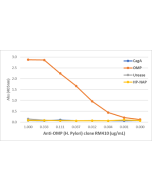
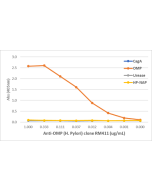
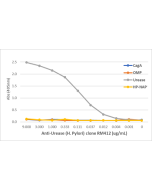
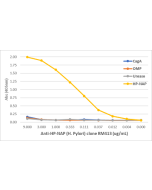
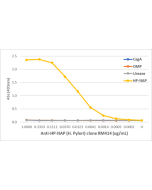
anti-Helicobacter pylori, Rabbit Monoclonal (RM429)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | H. Pylori; Campylobacter Pylori |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM429 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Proteins purified from Helicobacter pylori. |
| Application |
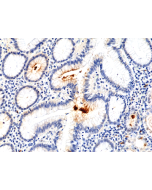
Immunohistochemistry (IHC): 1:100-1:200 dilution |
| Crossreactivity | Helicobacter pylori |
| Specificity |
RM429 reacts to Helicobacter pylori. |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Concentration | N/A |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterial class-I carcinogen that specifically colonizes the gastric epithelium of humans as a unique niche, where it can induce inflammatory disorders (e.g. ulceration, chronic gastritis, etc.) and malignant neoplastic diseases (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue [MALT] lymphoma and gastric cancer). To resist the hostile environment in the stomach, H. pylori has developed highly sophisticated mechanisms to establish life-long infections in the stomach if not therapeutically eradicated. Helicobacter pylori can exist in a number of locations: in the mucus; attached to epithelial cells; or inside of vacuoles in epithelial cells, where it produces adhesins that bind to membrane-associated lipids and carbohydrates to help its adhesion to epithelial cells. Helicobacter pylori contains a hydrogenase enzyme and obtains energy by oxidizing molecular hydrogen produced by other intestinal bacteria. It also excretes urease in order to convert urea into ammonia and bicarbonate which neutralizes the acidic environment of the stomach. Helicobacter pylori OMPs (outer membrane proteins) are involved in Helicobacter pylori adhesion and can cause signal transduction events in host cells. HP-NAP acts as a chemoattractant for nrutrophils, which produce oxygen radicals, cytokines and chemokines, crucial in driving the Th1 inflammation in H. pylori infection.