Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
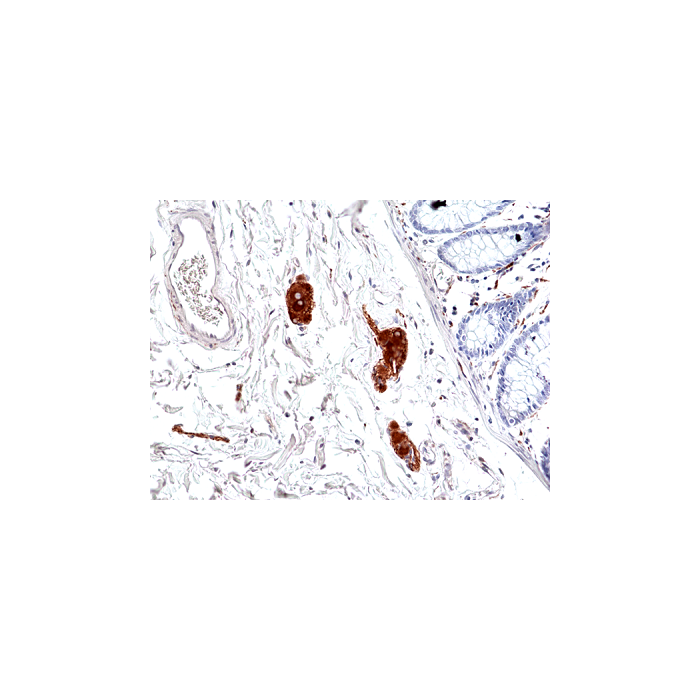
anti-Phospho-Tau (Ser396), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM461)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM461 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | A phospho-peptide corresponding to human Tau (Ser396). |
| Application |
Western Blot (WB): 1:1000-1:2000 |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse Rat |
| Specificity |
This antibody reacts to Tau only when phosphorylated at Ser396. There is no cross-reactivity to Tau that is not phosphorylated. This antibody reacts to human, mouse or rat Phospho-Tau (Ser396). |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Concentration | N/A |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Accession Number | P10636 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Tau is a neuronal microtubule-associated protein found predominantly on axons. The function of Tau is to promote tubulin polymerization and stabilize microtubules. The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N- terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker protein between both. Axonal polarity is predetermined by TAU/MAPT localization (in the neuronal cell) in the domain of the cell body defined by the centrosome. The short isoforms allow plasticity of the cytoskeleton while the longer isoforms may preferentially play a role in its stabilization. In its hyper-phosphorylated form, Tau is the major component of paired helical filaments (PHF), the building block of neurofibrillary lesions in Alzheimer's diseases (AD) brain. Hyper-phosphorylation impairs the microtubule binding function of Tau, resulting in the destabilization of microtubules in AD brains, ultimately leading to the degeneration of the affected neurons. Numerous serine/threonine kinases phosphorylate Tau, including GSK-3β, protein kinase A (PKA), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) and casein kinase II. Hyper-phosphorylated Tau is found in neurofibrillary lesions in a range and other central nervous system disorders such as Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy.





