Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
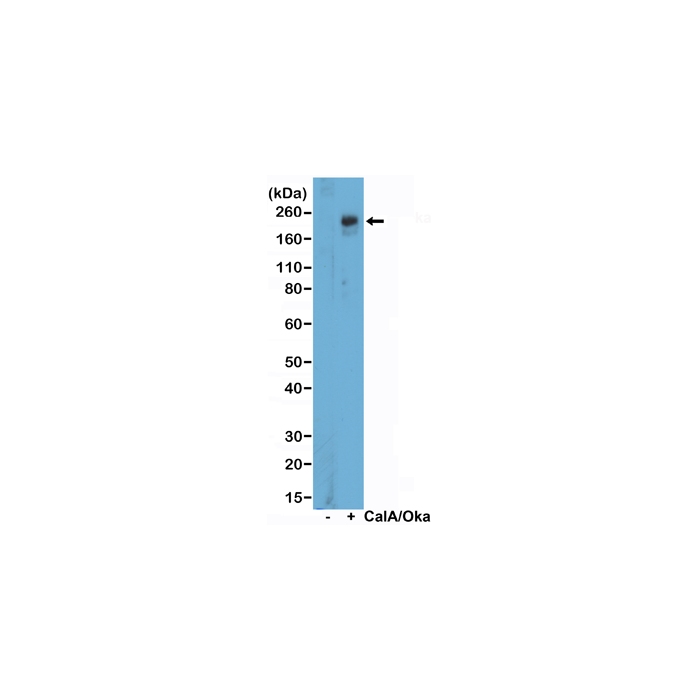
anti-Phospho-ULK1 (Ser757), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM488)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Unc-51-like Kinase 1; Autophagy-related Protein 1; ATG1 |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM488 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | A phospho-peptide corresponding to human phospho-ULK1 (Ser757). |
| Application |
Western Blot (WB): 1:1000-1:2000 dilution |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse Rat |
| Specificity |
This antibody reacts to human ULK1 only when phosphorylated at Ser757. There is no cross-reactivity to ULK1 that is not phosphorylated. This antibody may also react to mouse or rat Phospho-ULK1 (Ser757) as predicted by immunogen homology. |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Concentration | N/A |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Accession Number | O75385 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
ULK1, also known as ATG1, is a key serine/threonine protein kinase probably acting at the most upstream step of autophagosome formation. Knockout of ULK1 results in a severe defect in the autophagy pathway. ULK1 is highly conserved among eukaryotes, and are the Unc-51-like kinases, ULK1 and ULK2 in mammals. ULK1 is ubiquitously expressed and involved in autophagy in response to starvation. It is the target of the TOR kinase signaling pathway that regulates autophagy through the control of phosphorylation status of ATG13. ULK1 also plays a role early in neuronal differentiation.





