Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
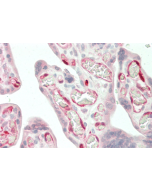
anti-IDO1 (human), pAb
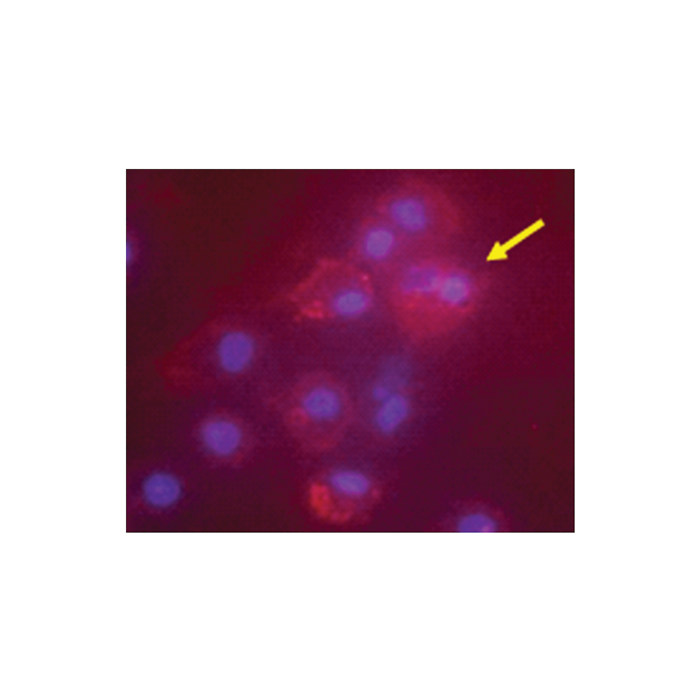
1. Recombinant human IDO1 (His tagged).
2. PHA- treated human peripheral blood lymphocyte lysate.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; IDO; INDO |
| Product Type | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Recombinant human IDO1. |
| Application |
ELISA: (direct and indirect: 1:2’000-1:10’000) |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Specificity |
Recognizes human IDO1. Detects a band of ~45kDa by Western blot. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A-affinity purified. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. 0.2μm-filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Contains no preservatives. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Accession Number | P14902 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
IDO1 is a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the main pathway of human tryptophan catabolism, the kynurenine pathway, causing depletion of tryptophan which can lead to halted growth of microbes as well as T cells. IDO1 is an immune checkpoint protein, thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation and antioxidant activity. Cancer cells are able to evade the immune system is by hijacking the checkpoint proteins. Increased IDO1 protein levels drive growth arrest and apoptosis of the effector T cells, a group of immune cells that mediate the immune system’s ability to destroy pathogens. By reducing the number of effector T cells, IDO1 overexpression prevents the immune system from effectively destroying cancer cells. IDO1 overexpression has been observed in a wide range of human cancers such as prostatic, colorectal, pancreatic, cervical, gastric, ovarian, head or lung cancer. Physiological IDO1 activity has been implicated in T cell tolerance to tumors, dysfunctional selftolerance in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, and as a protective negative regulator in autoimmune disorders.
- HIV inhibits CD4+ T-cell proliferation by inducing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in plasmacytoid dendritic cells: A. Boasso, et al.; Blood 109, 3351 (2007)
- Functional Alteration of the Lymphoma Stromal Cell Niche by the Cytokine Context: Role of Indoleamine-2,3 Dioxygenase: H. Maby-El Hajjami, et al.; Cancer Res. 69, 3228 (2009)
- A novel cancer therapy by skin delivery of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase siRNA: M.C. Yen, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 641 (2009)
- Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing leukemic dendritic cells impair a leukemia-specific immune response by inducing potent T regulatory cells: A. Curti, et al.; Haematologica 95, 2022 (2010)
- The indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor 1-methyl-D-tryptophan upregulates IDO1 in human cancer cells: C.A.Opitz, et al.; PLoS One 6, e19823 (2011)
- Melanoma cells inhibit natural killer cell function by modulating the expression of activating receptors and cytolytic activity: G. Pietra, et al.; Cancer Res. 72, 1407 (2012)
- Inhibition of Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in Glioblastoma Cells by Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus: B. Reinhart, et al.; Adv. Virol. 2012, 815465 (2012)
- An Autocrine Cytokine/JAK/STAT-Signaling Induces Kynurenine Synthesis in Multidrug Resistant Human Cancer Cells: I. Campia, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0126159 (2015)
- Tumor indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibits CD19-CAR T cells and is downregulated by lymphodepleting drugs: S. Ninomiya, et al.; Blood 125, 3905 (2015)
- Targeting of Janus Kinases Limits Pro-Inflammatory but Also Immunosuppressive Circuits in the Crosstalk between Synovial Fibroblasts and Lymphocytes: N. Yao, et al.; Biomedicines 9, 1413 (2021)