Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
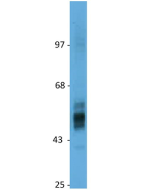
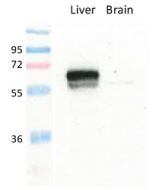
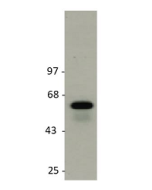
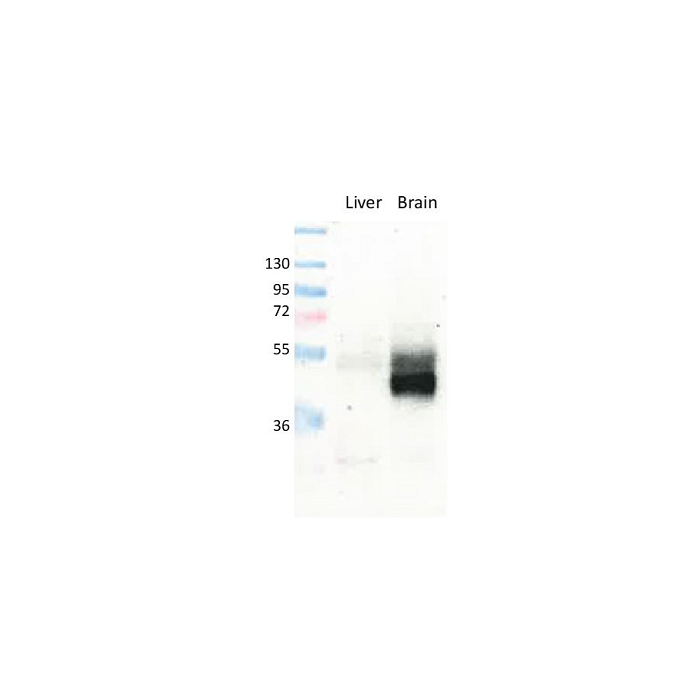
anti-GLUT1, pAb (IN116)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Solute Carrier Family 2, Facilitated Glucose Transporter Member 1; SLC2A1; Glucose Transporter Type 1, Erythrocyte/Brain; HepG2 Glucose Transporter |
| Product Type | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | A synthetic peptide corresponding to 15 aa located near the C-terminus of human GLUT1. |
| Application |
Western Blot: (1:500)* |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse Rat |
| Specificity |
Recognizes human, mouse and rat GLUT1. Does not detect GLUT2. |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS containing 10% glycerol and 0.02% Proclin 300. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link P11166: GLUT1 (human) |
| Accession Number | P11166 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
GLUT1 belongs to the family of glucose transporters (GLUTs, encoded by the SLC2A genes), which comprises 14 isoforms. GLUT1, the uniporter protein encoded by the SLC2A1 gene, is a key rate-limiting factor in the transport of glucose. It is composed of twelve transmembrane segments of the protein and an intracellular N- and C-terminus are forming the protein pore. In normal tissues, GLUT1 is limited to being expressed on erythrocytes and endothelial cells in the blood-brain barriers. GLUT1 is located at the blood-brain barrier and assures the transport of glucose (the most important energy carrier of the brain) into the brain. The genetic defect of Glut1 is known as the Glut1 deficiency syndrome (Glut1-DS) and is characterized by early infantile seizures, developmental delay, microcephaly and ataxia.
GLUT1 is a pivotal rate-limiting element in the transport of glucose in malignancy cells and is overexpressed in different types of human cancers. GLUT1 is involved in the progression and metastasis of cancer cells.
- Expression of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter in Escherichia Coli: H.K. Sarkar, et al.; PNAS 85, 5463 (1988)
- Differential localization of two glucose transporter isoforms in kidney: B. Thorens, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. 259, C286 (1990)