Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
APRIL (human) (multimeric) (rec.)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MultimericAPRIL™; ACRP30headless:APRIL; ACRP30headless:CD256; ACRP30headless:TNFSF13; ACRP30headless:A-proliferation-inducing Ligand: |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | HEK 293 cells |
| Sequence |
The extracellular domain of human APRIL (aa 88-233) is fused at the N-terminus to human ACRP30headless (aa 16-108) and a FLAG®-tag. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Specificity |
Binds to human and mouse BCMA and TACI. Binds to proteoglycans. |
| Biological Activity |
Stimulates B cell proliferation. |
| MW | ~36kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza). |
| Concentration | 0.1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 100μl sterile water. |
| Accession Number | O75888 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link O75888: APRIL (human) FLAG is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
APRIL is a cytokine that belongs to the TNF superfamily and binds to TACI and BCMA. It is implicated in the regulation of tumor cell growth, is involved in monocyte/macrophage-mediated immunological processes and functions as an important survival factor for plasmablasts and bone marrow plasma cells.
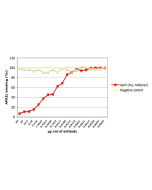
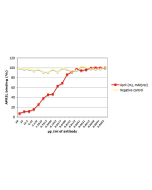
MultimericAPRIL™ is a high activity construct in which two trimeric APRIL ligands are artificially linked via the collagen domain of ACRP30. This construct very effectively stimulates proliferation B cell. A basic amino acid sequence (QKQKKQ) close to the NH2 terminus of APRIL is required for binding to negatively charged sulfated glycosaminoglycan side chains of proteoglycans. Proteoglycans mediate binding of APRIL to tumor cells as well as primary lymphoid cells.
- DCs induce CD40-independent immunoglobulin class switching through BLyS and APRIL: M.B. Litinskiy, et al.; Nat. Immunol. 3, 822 (2002)
- APRIL modulates B and T cell immunity: J.V. Stein, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 109, 1587 (2002)
- Potential role of APRIL as autocrine growth factor for megakaryocytopoiesis: D. Bonci, et al.; Blood 104, 3169 (2004)
- Lymphoma B cells evade apoptosis through the TNF family members BAFF/BLyS and APRIL: B. He, et al.; J. Immunol. 172, 3268 (2004)
- BAFF regulates B cell survival by downregulating the BH3-only family member Bim via the ERK pathway: A. Craxton, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 202, 1363 (2005)
- APRIL and BAFF promote increased viability of replicating human B2 cells via mechanism involving cyclooxygenase 2: P.K. Mongini, et al.; J. Immunol. 176, 6736 (2006)
- TACI regulates IgA production by APRIL in collaboration with HSPG: D. Sakurai, et al.; Blood 109, 2961 (2007)
- BAFF and APRIL support chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cell survival through activation of the canonical NF-kappaB pathway: T. Endo, et al.; Blood 109, 703 (2007)
- STAT-3 Activation by Differential Cytokines Is Critical for Human In Vivo-Generated Plasma Cell Survival and Ig Secretion: B. Rodriguez-Bayona, et al.; J. Immunol. 191, 4996 (2013)
- The immunoregulator soluble TACI is released by ADAM10 and reflects B cell activation in autoimmunity: F.S. Hoffmann, et al.; J. Immunol. 194, 542 (2015)
- Myelopoiesis dysregulation associated to sustained APRIL production in multiple myeloma-infiltrated bone marrow: T. Matthes, et al.; Leukemia 29, 1901 (2015)
- TNF superfamily member APRIL enhances midbrain dopaminergic axon growth and contributes to the nigrostriatal projection in vivo: T.G. McWilliams, et al.; Exp. Neurol. 298, 97 (2017)
- APRIL limits atherosclerosis by binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans: D. Tsiantoulas, et al.; Nature 597, 92 (2021)