Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
IL-36α (human) ELISA Kit
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Interleukin-1 Family Member 6; IL-1F6 |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity |
Detects natural and recombinant human IL-36α (IL-1F6). |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity |
1 x 96 wells |
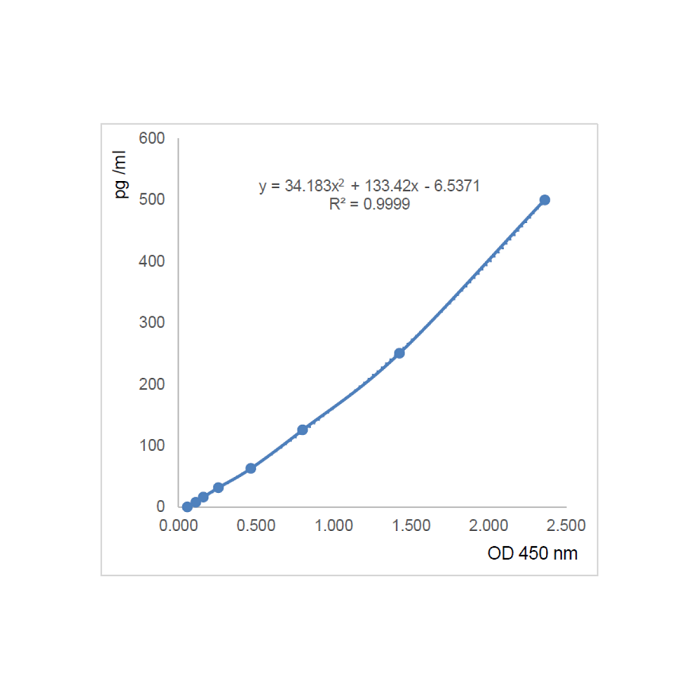
| Sensitivity | 4pg/ml |
| Range | 7.8 to 500pg/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Plasma Serum |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link Q9UHA7: IL-36α (human) |
| Accession Number | Q9UHA7 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
IL-36α (IL-1F6), IL-36β (IL-1F8) and IL-36γ (IL-1F9) are members of the IL-1 cytokine family that bind to IL-36R (IL-1Rrp2) and IL-1RAcP, activating similar intracellular signals as IL-1 and are inhibited by IL-36Ra. IL-36α, β and γ cytokines, similarly to IL-1β, need to be processed to acquire their full agonist or antagonist activity. Neutrophils proteases have been identified as the chief regulators of the processing of all the IL-36 family members, although with different specificity and affinity. IL-36α seems to be activated by both neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G, however, with differential patterns. The expression of IL-36 cytokines occurs mainly in the lung and skin and can be derived from diverse epithelial cell types including keratinocytes, bronchial epithelium as well as macrophages, monocytes and different T cell subsets. IL-36 family members induce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-12, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and IL-23, thus promoting neutrophil influx, dendritic cell (DC) activation, polarization of T helper type 1 (Th1) and IL-17-producing T cells (αβ T cells and γδ T cells) and keratinocyte proliferation. The IL-36 cytokines may represent potential targets for immune-mediated inflammatory conditions or, alternatively, could be used as adjuvants in vaccination. IL-36α and IL-36β augmented IL-17A-mediated induction of antibacterial peptides in psoriasis. A significant increase in circulating and tissue levels of IL-36α occurs in Sjögren’s syndrome patients. An increased expression of IL-36α and IL-36γ, but not IL-36β has been observed in colonic inflammatory lesions from patients with inflammatory bowel disease, more prominently in ulcerative colitis. Association between IL-36 and Th17 responses was also confirmed in Crohn’s disease, although the expression of IL-36 in this population was significantly lower than in psoriasis. All members of the IL-36 subfamily are expressed during estrous cycle and pregnancy. IL-36α has also been involved in the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma, where its expression correlates negatively with tumor size, degree of differentiation and level of vascular invasion. Correspondingly, high levels of IL-36α are positively correlated to the overall survival of patients.