Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
ICOSL (B7-H2/CD275) (human) ELISA Kit
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ICOS Ligand; B7 Homolog 2; B7-H2; CD275 |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity |
Detects soluble human ICOSL [B7-H2/CD275] in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatant. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity |
1 x 96 wells |
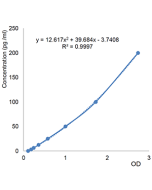
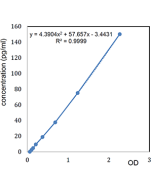
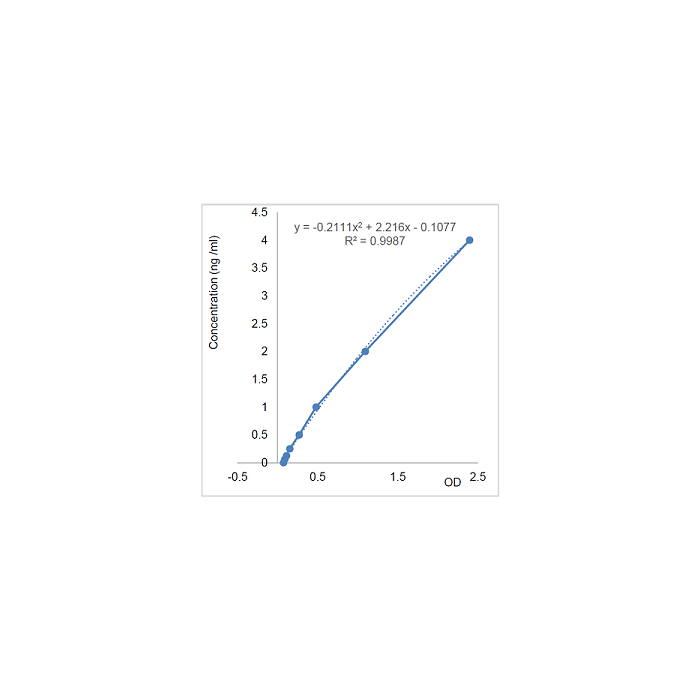
| Sensitivity | 55pg/ml |
| Range | 0.0625 to 4 ng/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Plasma Serum |
| Assay Type | Sandwich |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link O75144: ICOSL (human) |
| Declaration | In collaboration with Suzhou Bright Scistar Biotechnology |
| Accession Number | O75144 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Inducible T-cell costimulatory protein (ICOS, also called CD278, AILIM, H4), a member of the CD28 family of costimulatory receptors, has a role in the generation and maintenance of germinal centers (GCs) in lymphatic organs, induction of thymus-dependent (TD) antibody (Ab) responses and antibody class switching. ICOS has a low expression on naïve T cells but is rapidly induced on activated T cells. ICOS binds to the inducible co-stimulator ligand (ICOSL, also called CD275, B7-H2, B7h, B7RP-1) that is found in professional APCs such as dendritic cells (DCs), B lymphocytes, various non-hematopoietic cells such as endothelial cells (ECs), as well as some cancer cells. ICOS activated by ICOSL induces T cell proliferation, survival and differentiation and co-induces the secretion of IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-21, TNF-α and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) (whereas CD28 induces IL-2 production). Therefore, ICOS enhances Th1, Th2, and Th17 function largely through augmented production of these effector cytokines. ICOSL is upregulated by TNF-α and other inflammatory mediators and has an important co-stimulation role in EC (endothelial cells)-mediated T-cell activation, especially in reactivation of effector/memory T cells on the endothelium, which promote the homing of immune cells into inflamed tissue. As seen in diverse types of costimulatory molecules in the CD28 family in T cells, ICOS is able to deliver a reverse signal through ICOSL that has a direct effect on dendritic cells. ICOS /ICOSL is involved in some hematologic malignancies such as myeloma or lymphoma. ICOS and its ligand (ICOSL) have been shown to play diverse roles in mediating autoimmunity as well as enhancing the development/activity of regulatory T cells. ICOS has a dual role in oncogenesis: i) the costimulatory signal of ICOS/ICOSL clearly participates to an antitumor T-cell response; ii) the ICOS signaling also exhibits pro-tumoral features, which are related to the induction of Treg immunosuppressive effect. In humans, homozygous ICOS deficiency results in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), a condition characterized by aberrantly low serum gammaglobulin concentration. ICOS/ICOSL pathway is necessary for the optimal therapeutic effect of anti-CTLA-4, thus implicating this pathway as a target for future combinatorial strategies to improve the efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 therapy. ICOSL sheds from the cell membrane and the soluble form of ICOSL (sICOSL), found in plasma and sera, can be a potential biomarker for autoimmune diseases and some cancers.
- Development of a novel monoclonal antibody to human inducible co-stimulator ligand (ICOSL): Biological characteristics and application for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: X. Hu, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 36, 151 (2016)