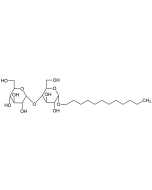Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
n-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside (high purity)
As low as
70
CHF
CHF 70.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CC1-0010-G0011 gCHF 70.00
AG-CC1-0010-G0055 gCHF 195.00
AG-CC1-0010-G02525 gCHF 720.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DDM; n-Dodecyl-β-maltoside; Lauryl-β-maltoside; Dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C24H46O11 |
| MW | 510.6 |
| CAS | 69227-93-6 |
| Purity Chemicals |
≥99% (HPLC) [α-Anomer <2.0% (NMR)] [n-Dodecanol <0.005% (HPLC)] |
| Appearance | White powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water or 100% ethanol. |
| InChi Key | NLEBIOOXCVAHBD-QKMCSOCLSA-N |
| Smiles | CCCCCCCCCCCCOC1OC(CO)C(OC2OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C1O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Hygroscopic. Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 3 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Water-soluble non-ionic detergent with a hydrophilic maltose head and a hydrophobic long chain alkyl tail. It is considered a gentle detergent that is more efficient than other detergents.
- For functional solubilization and purification of membrane proteins. It helps to retain the native conformation and activity of membrane-associated proteins and facilitates the reforming of these proteins after denaturation.
- For the stabilization and activation of enzymes.
- The critical micelle concentration of DDM is approx. 0.18 mM in water, decreases in the presence of sodium chloride or sucrose and increases in urea.
Product References
- Synthesis and properties of some α-D-alkyl glucosides and mannosides: apparent molal volumes and solubilization of nitrobenzene in water at 25°C: G.M. Brown, et al.; Can. J. Chem. 48, 2525 (1970)
- Detergent-mediated reconstitution of membrane proteins: J. Knol, et al.; Biochem. 37, 16410 (1998)
- The vesicle-to-micelle transition of phosphatidylcholine vesicles induced by nonionic detergents: Effects of sodium chloride, sucrose and urea: A. Walter, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1508, 20 (2000)
- Macromolecular Crystallography Protocols: S. Doublie; Methods Mol. Biol. 363, (2007)
- Detergents for the stabilization and crystallization of membrane proteins: G.G. Prive; Methods 41, 388 (2007)
- The use of detergents to purify membrane proteins; T. Arnold & D. Linke; Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. Chapter 4: Unit 4.8.1-4.8.30 (2008)
- Expression, purification and in vitro functional reconstitution of the chemokine receptor CCR1: S.J. Allen, et al.; Prot. Expr. Purif. 66, 73 (2009)
- Structuring detergents for extracting and stabilizing functional membrane proteins: R. Matar-Merheb, et al.; PLoS One 6, e18036 (2011)
- Efficiency of detergents at maintaining membrane protein structures in their biologically relevant forms: D.V. Tulumello & C.M. Deber; Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1818, 1351 (2012)
- High-throughput stability screening for detergent-solubilized membrane proteins: V. Kotov, et al.; Sci. Rep. 9, 10379 (2019)